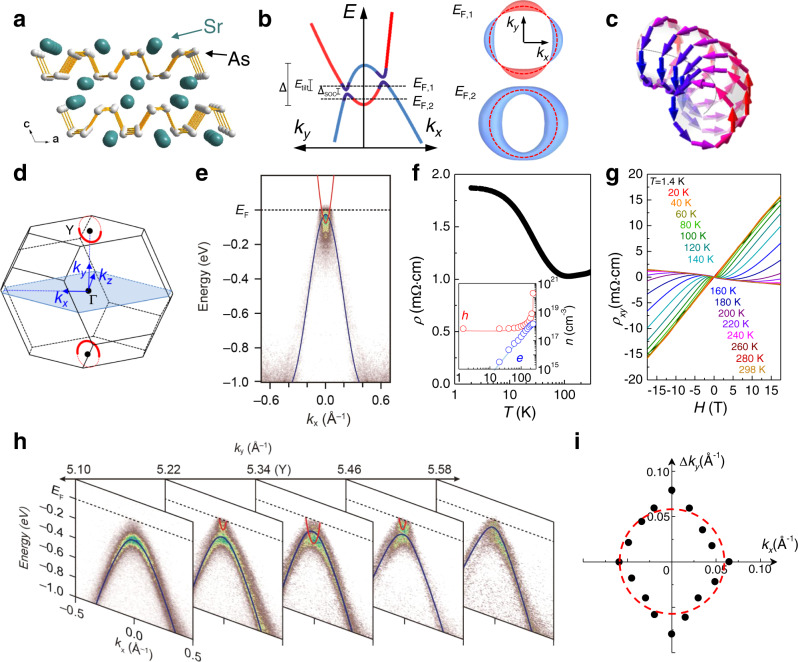
Fig. 1. Crystal and electronic structures of a nodal-line semimetal SrAs3.
a The crystal structure of SrAs3. b The schematic band crossing for asymmetric nodal-line states with a tilted energy dispersion (Etilt), a finite spin–orbit-coupling gap (ΔSOC) and a band overlap energy (Δ). The corresponding Fermi surfaces at different Fermi levels (EF) are shown in the right, a crescent-type for EF,1 and a torus-type for EF,2. c The smoke-ring-type pseudospin texture imprinted on the Fermi surface. d The Brillouin zone of SrAs3 with a single nodal ring (red circle) centered at the Y point. e The ARPES spectra of SrAs3 taken at the Y point along kx with the photon energy of 99 eV. The overlaid red and blue lines indicate the conduction and valence bands, respectively. f The temperature dependence of the in-plane resistivity (ρ). The inset shows the carrier densities (n) for electron (e) and hole (h). g The magnetic field-dependent Hall resistivity (ρxy) of SrAs3 at different temperatures. h A series of ARPES spectra taken along kx at different photon energies (85-104 eV) corresponding to ky marked on top of each panel. i The nodal-ring of the crossing points between the conduction and valence bands in ARPES data, with dashed red circle as a guide to the eye.