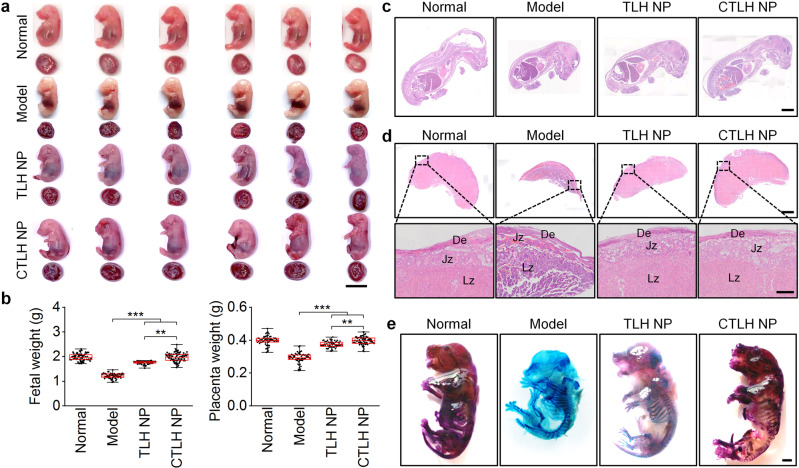
Fig. 9. Inhibition of DVT-induced embryonic developmental disorders and early fetal growth delay in pregnant rats by the active targeting nanotherapy CTLH NP.
a Digital photos of representative rat fetuses and placentas from normal or DVT pregnant rats at G17. One fetus or placenta was randomly selected from each rat of different groups (n = 6 independent animals). Scale bar, 1 cm. b Fetal and placental weights of different groups. Both fetuses and placentas were from 6 pregnant rats in each group (independent animals). c H&E-stained histological sections of isolated fetuses at G17. Scale bar, 4 mm. d Whole slide and high-magnification images of H&E-stained placental sections. Scale bars, 2 mm (upper) and 500 μm (lower). De, decidua; Jz, junctional zone; Lz, labyrinth zone. e Whole-mount skeletal staining of fetuses via Alizarin red and Alcian blue. Scale bar, 200 μm. In this study, stenosis-induced DVT in pregnant rats was established at G10. After thrombus formation, pregnant rats in the model group were treated with saline, while other two groups were separately administered with TLH NP and CTLH NP at 5 mg/kg of LMWH by daily i.v. injection for 5 days. For the normal group, healthy pregnant rats with the sham operation were treated with saline. All fetuses and placentas were excised from uteruses at G17 for analyses. Data in box plots b show the mean value and extend from 25 to 75%, while the whiskers extend from the minimal to maximal values, which are based on all fetuses and placentas from six pregnant rats in each group. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA with post hoc LSD tests. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data in c–e are representative of six independent samples. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.