Figure 1.
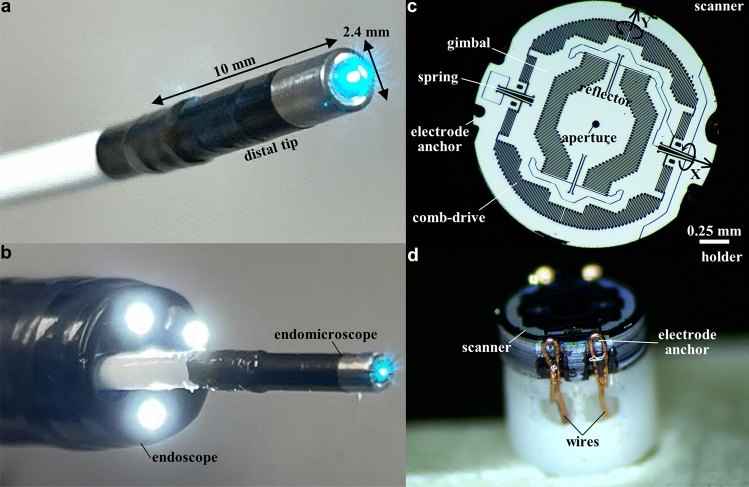
Confocal laser endomicroscope (CLE) and MEMS scanner. Photo is shown of (a) the packaged instrument with rigid distal tip dimensions of 2.4 mm in diameter and 10 mm in length, and (b) forward passage through the working channel of a standard medical endoscope (Olympus CF-HQ190L). (c) Front view of the scanner shows a reflector with a 50 μm diameter central aperture to allow excitation beam to pass. The scanner is mounted on a gimbal driven by a set of orthogonal comb-drive actuators. The resonance frequencies of this device are determined by the dimensions of the torsional springs. (d) Side-view of the scanner shows scanner mounted on the holder with wires to electrode anchors that provide points of connection for the drive signals and power.