Figure 2.
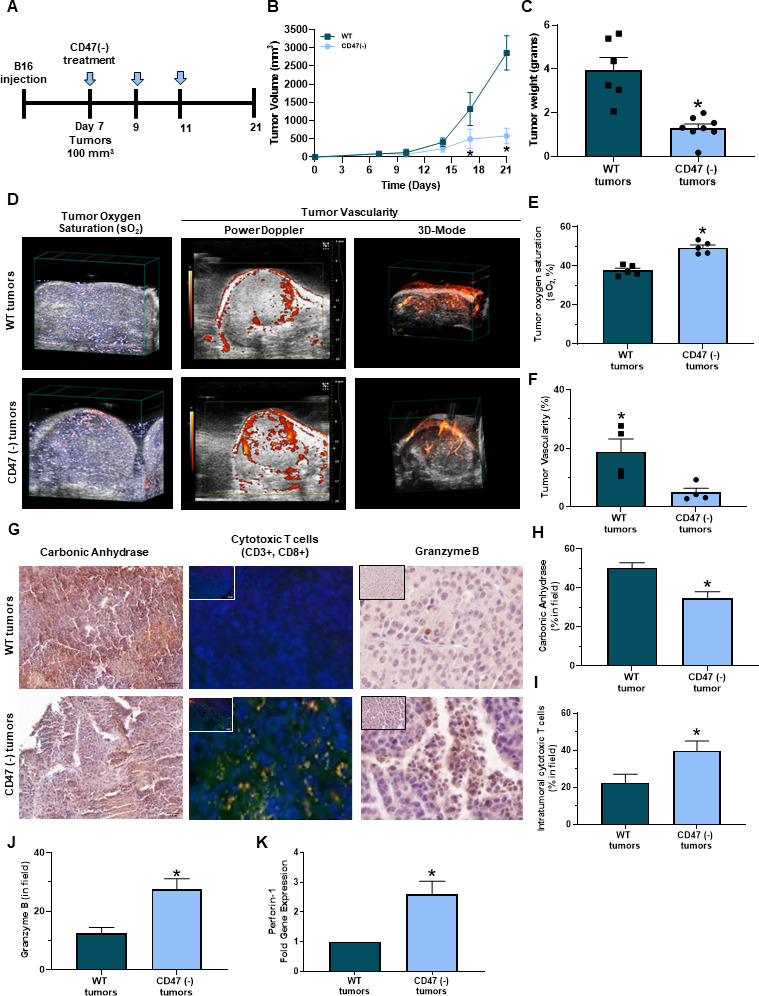
Targeting CD47 decreases melanoma tumor burden in vivo. (A) Schematic of the in vivo syngeneic mouse melanoma treatment regimen. C57Bl/6 mice were injected subcutaneously with B16 melanoma cells into the hind flank. Once tumors reached 100 mm3, intraperitoneal injections of 10 uM CD47 morpholino (CD47(-)) or saline began once a week for 3 weeks. (B) Tumor volume was determined throughout the study (LW2/2). (C) Mice were euthanized at the end of the study (day 21) or when tumor volume reached 1500 mm3 where tumor weight was determined (*p<0.05, n=6–8/group). (D) Representative PAI imaging for tumor sO2 along with Power Doppler in 3D-Mode to determine tumor vascularity. (E) Tumor sO2 was quantified with the Vevo 2100 LAZR software tools while (F) tumor vascularity was quantified with Vevo CQ software of WT and CD47 targeted tumors (*p<0.05, n=4–5/group). (G) Representative immunohistochemistry images of tumor sections for (H) carbonic anhydrase, (I) intratumoral cytotoxic (yellow cells due to colocalization of CD3+ (red, APC) and CD8+ (green, FITC) T cells and (J) granzyme B (*p<0.05, n=4–5/group). Images were obtained at 20x magnification with the Olympus BX43 microscope and quantified using the PerkinElmer Mantra and inform analysis. (K) Gene expression of perforin-1 was determined through RT-qPCR of tumors (*p<0.05, n=4–5/group). PAI, photoacoustic imaging; WT, wild type.
