TABLE 1.
Compounds used in this work.
| Compounds | Bioavailability radar | Predicted LD50 [mg/kg] (predicted toxicity class) |
|---|---|---|
11, LogP 2.56
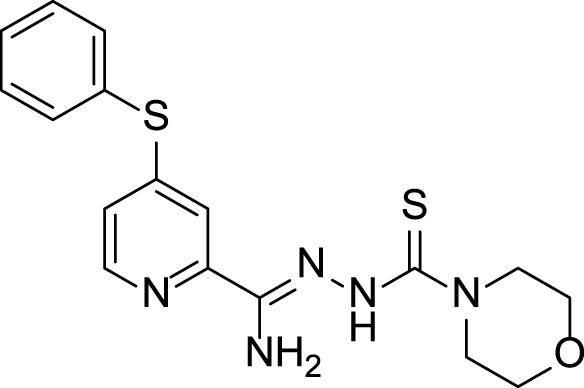
|
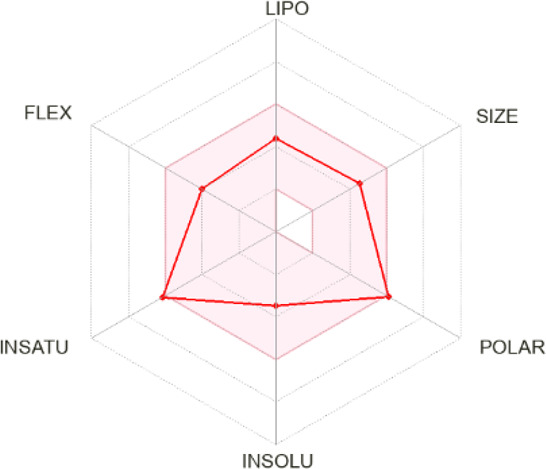
|
70 (3) for neutral form |
| 3500 (5) for zwitterion | ||
15, LogP 1.06
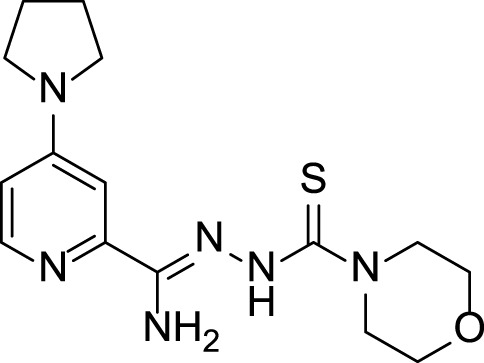
|
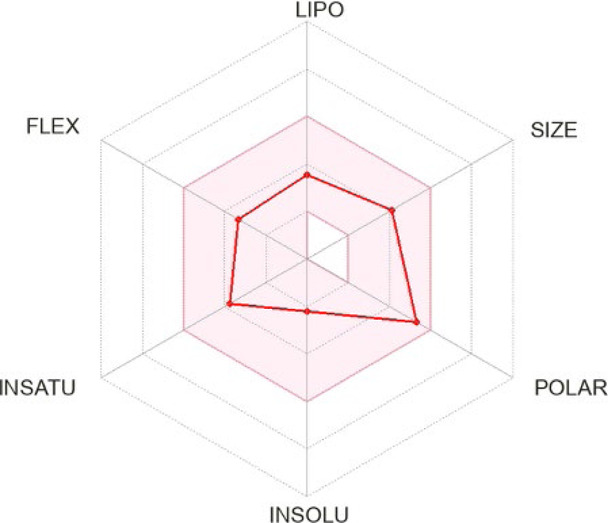
|
3 (1) for neutral form |
| 1,600 (4) for zwitterion |
Bioavailability radar was used to determine the drug-likeness of the tested compounds. The prediction LD50 method is based on the analysis of the two-dimensional similarity to compounds with known LD50 values and the identification of fragments overrepresented in toxic compounds. LD50 values are given in [mg/kg]. Class I: fatal if swallowed (LD50 ≤ 5), Class II: fatal if swallowed (5 < LD50 ≤ 50), Class III: toxic if swallowed (50 < LD50 ≤ 300), Class IV: harmful if swallowed (300 < LD50 ≤ 2000), Class V: may be harmful if swallowed (2000 < LD50 ≤ 5,000), Class VI: nontoxic (LD50 > 5,000).- lipophilicity (LIPO) is within the range -0.7 < XlogP3 < +5.0; molecular weight (SIZE) is 150 g/mol < MW < 500 g/mol; polarity (POLAR) is 20 Å2 < TPSA <130 Å2; insolubility (INSOLU) is 0 < logS <6; insaturation (INSATU) is 0.25 < fraction Csp3 < 1; and flexibility (FLEX) is 0 < Num rotatable bonds <9). For drug-like properties, compounds were found to have a good bioavailability score (0.55) (Lipinski et al., 2012), which is consistent with Lipiński’s rule of five. This compound meets the rules of Lipinski, Ghose, Veber and Muegge (Ghose et al., 1999; Muegge et al., 2001; Veber et al., 2002; Lipinski et al., 2012). Shown in the BOILED-Egg diagram, the test samples do not pass the blood–brain barrier but are absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. The compounds are not available through the skin, as indicated by a negative logKp value (-7.84 cm/s). The ProTox II, webserver classified the toxicity classes of the ligands.
