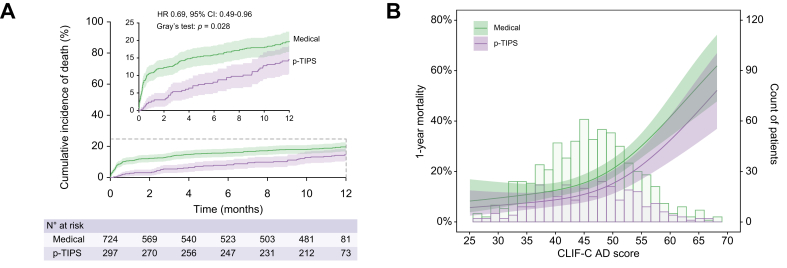
Fig. 1.
Competing risks analyses for all-cause mortality in entire cohort and the relationship between the mortality risk and CLIF-C AD scores stratified by treatment groups.
(A) Cumulative incidence of death in pre-emptive TIPS vs. medical groups (p = 0.028, Gray’s test) based on competing risk approach (the Fine and Gray method) with liver transplantation being the competing event. (B) Probability of death within 1 year and patient distribution in relation to CLIF-C AD score stratified by treatment groups (p = 0.042, logistic regression analysis). Restricted cubic splines were generated using logistic regression models after adjusting for active bleeding at endoscopy (yes vs. no), serum albumin (per g/L increase), platelet count (per 1 × 109/L increase), comorbidities (yes vs. no), infection (yes vs. no), and shock (yes vs. no). The coloured bands indicate 95% CIs. CLIF-C ADs, Chronic Liver Failure-Consortium acute decompensation score; HR, hazard ratio; p-TIPS, pre-emptive transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.