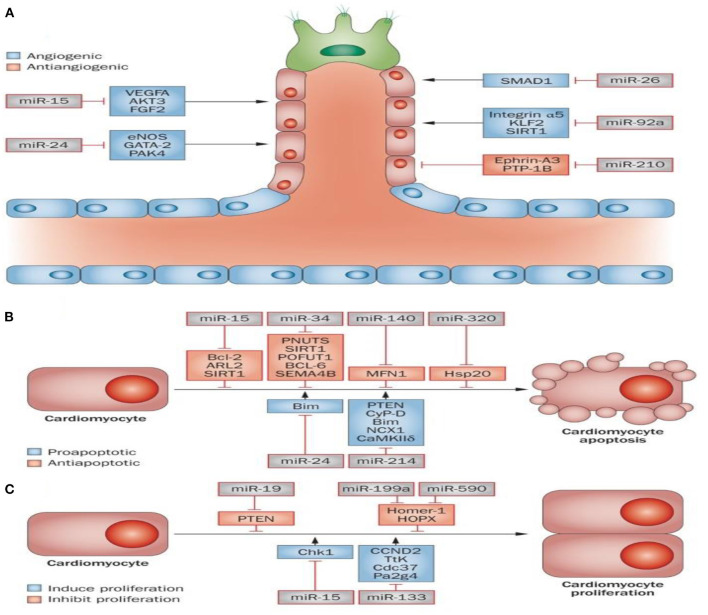
Figure 1.
Role of microRNAs in MI. Some miRNAs are known to be implicated in cardiac muscle angiogenesis (A), cardiac cell survival, and proliferation (B,C). Angiogenesis is pivotal for the delivery of oxygen and essential nutrients to heart muscle. Angiogenesis can be activated or repressed by a number of microRNAs. For instance, miR-15, miR-24, miR-26, and miR-92a all repress angiogenesis through inhibition of endothelial-cell functions. In contrast, miR-210 prompts angiogenesis via inhibiting several antiangiogenic factors (A). A number of miRNAs have been identified to be involved in the apoptosis and survival of cardiac cells. Apoptosis inhibition or an increase in survival signals promotes cardiac regeneration. The miR-15 family (miR-320, miR-34, and miR-140) can serve as pro-apoptotic factors, while miR-24 and miR-214 can act as anti-apoptotic factors (B). The proliferation of cardiac cells is limited; however, cardiac regeneration can increase following stimulation of proliferation. It has been shown that miR-19, miR-199a and miR-590, can promote proliferation of cardiac cells, while both miR-15 and miR-133 inhibit cardiac cell proliferation (C). This figure adapted from Boon and Dimmeler (76).