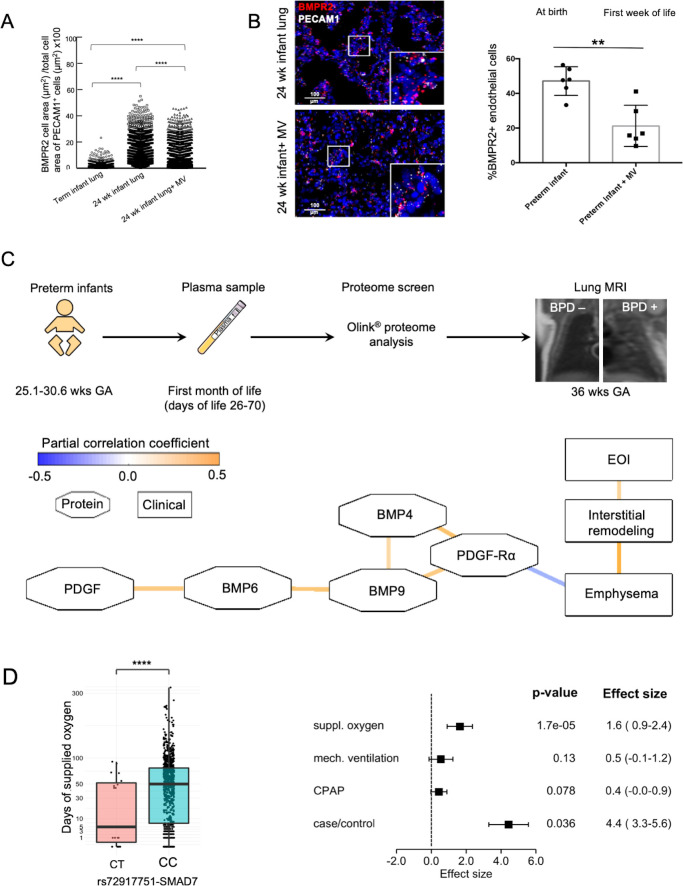
Figure 1.
Decrease in lung vasculature BMPR2 expression and reduced BMP and PDGF plasma levels in preterm infants with BPD in the absence of relevant genetic variants. ISH quantification of BMPR2 and PECAM1 +double positive cells (positive cell area/total cell area; µm2/µm2) showed (A) the physiological increase in BMPR2 expression per endothelial cell in the developing preterm lung when compared with a term newborn as well as the decrease with mechanical ventilation (MV) in a preterm infant at the same age, that is, 24 weeks gestational age (GA) and (B) a significant reduction of overall pulmonary microvascular BMPR2 expression in the preterm infant undergoing postnatal lung injury induced by the exposure to MV for 2–8 weeks (24–26 weeks GA at birth; n=3/group) when compared with age-matched infants who died in the first days of life. (C) EDTA plasma samples were obtained in preterm neonates GA 25.1–30.6 weeks) with (1) and without (0) BPD at days of life 26–70 and subjected to proteome analysis (Olink proteomics). Infants were characterised for their lung structural changes at term by lung MRI (T2-weighted single-shot fast-spin-echo (ssFSE) sequences;) MRI left panel: infant without BPD, MRI right panel: infant with severe BPD in coronal plane showing interstitial enhancement and emphysematous changes. The partial correlation network of log2 transformed protein expression profile obtained by proteome analysis (day of life 28+) reveals a negative correlation between the protein levels of the BMPR2 and PDGF-Rα signalling cascade and the development of emphysema and interstitial remodelling. The network accounts for BPD, days of MV, days of O2 supplementation and GA (blue line: negative correlation, orange line: positive correlation; octagons: proteins, rectangles: clinical variables). All edges are significant at false discovery rate (FDR)<0.25. (D) Association of rs72917751-SMAD7 with time of supplemented O2. Rounded gene doses for the rs72917751 genotypes (imputed). association analysis was done using area sinus hyperbolicus transformed values of the time of supplemented oxygen (p=1.7×10−5, FDR=0.48). Association was adjusted for relatedness, gender, gestational age, birth weight <10 th percentile, and country of maternal origin. Effect size of rs72917751-SMAD7 in human genetic association analysis. Association of rs72917751 was investigated with BPD case–control status and three measures of respiratory support (area sinus hyperbolicus transformed). Phenotypes were adjusted for relatedness, gender, gestational age, birth weight <10 th percentile and country of maternal origin. Data are mean±SD **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001. BMPR2, bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2; BPD, bronchopulmonary dysplasia; ISH, RNA in situ hybridization.