Table 1. Characterization of the Polymers Obtained in This Study by RAFT Polymerization.
| polymer | conv. % (NMR)a | Mn (GPC) g mol–1 × 10–3 | Mn (calc)bg mol–1 × 10–3 | Đ(GPC) Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G275 | >95 | 8.2 | 14.1 | 1.08 |
| H66-b-G275 | 88 | 15.7 | 28.2 | 1.17 |
| G475 | >95 | 11.0 | 22.5 | 1.12 |
| H38-b-G475 | 92 | 16.3 | 30.6 | 1.19 |
| H73-b-G475 | 73 | 18.6 | 38.0 | 1.20 |
| G975 | >95 | 13.7 | 37.5 | 1.13 |
| H93-b-G975 | 93 | 23.3 | 57.3 | 1.15 |
| G269G96 | >95 | 8.8 | 16.0 | 1.09 |
| H75-b-G269G96 | >95 | 15.8 | 32.0 | 1.13 |
| G264G911 | >95 | 9.3 | 17.5 | 1.09 |
| H68-b-G264G911 | 90 | 16.0 | 32.0 | 1.14 |
| G253G922 | >95 | 10.0 | 21.0 | 1.08 |
| H45-b-G253G922 | 89 | 15.9 | 30.6 | 1.15 |
| H60-b-G253G922 | 80 | 15.5 | 33.8 | 1.15 |
| G222G953 | >95 | 12.2 | 30.6 | 1.11 |
| H67-b-G222G953 | 89 | 17.7 | 44.9 | 1.17 |
Conversion for OEGMA polymerization
or chain extension where applicable. NMR conversion values are calculated
as follows: 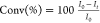 , where I0 and It are the intensities of the
vinyl signals from monomers at time = 0 and t, relative
to the terminal OEGMA signal −OCH3 (3H).
, where I0 and It are the intensities of the
vinyl signals from monomers at time = 0 and t, relative
to the terminal OEGMA signal −OCH3 (3H).
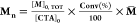 , where[M]0,TOT = sum of all monomers;
, where[M]0,TOT = sum of all monomers; 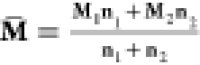 .
.
