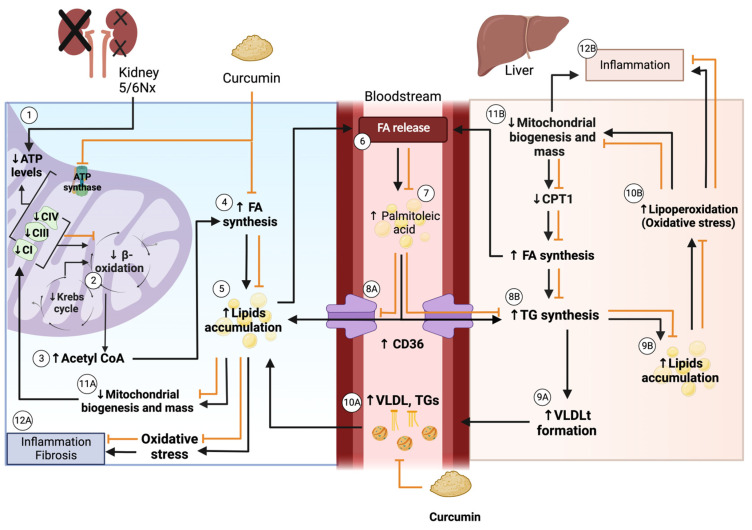
Figure 10.
Integrative scheme. (1) In kidney of 5/6 nephrectomy (5/6Nx), adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels are reduced, attributed to the decrease in the activity of electron transfer system (ETS) elements complex I (CI), CIII, and CIV, and ATP synthase [34]. (2) The decrease in the ETS reduces β-oxidation [18], which along with the reduction in the Krebs cycle, leads to (3) acetyl CoA accumulation [60]. This acetyl CoA is used for (4) fatty acids (FA) synthesis, inducing (5) lipid accumulation, and latter (6) FA release into the bloodstream, particularly (7) palmitoleic acid, which increases in the bloodstream and might (8A) reenter the kidney via a cluster of differentiation 36 (CD36), contributing to lipid accumulation [9]. On the other hand, palmitoleic acid might (8B) enter the liver by CD36, increasing triglycerides (TG) synthesis. TG synthesis increases (9A) the formation of VLDLt, or (9B) contributes to lipid accumulation in the liver. VLDLt proteins (10A) might be delivered in the bloodstream, which increases VLDL and TG levels that could go to the kidney and reinforce lipid accumulation. In the kidney, lipid accumulation (11A) decreases mitochondrial biogenesis and mass, decreasing ETS proteins. Besides, (9B) lipid accumulation in the liver promotes (10B) oxidative stress by inducing lipoperoxidation, which (11B) reduces mitochondrial biogenesis and mass, inducing the decrease in carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 (CPT1), and later, the increase in FA synthesis, which also induces FA releasing into the bloodstream. Oxidative stress and the reduction in biogenesis and mass contribute to inflammation and fibrotic process (12A) in the kidney and (12B) liver. Curcumin increases the ETS system and β-oxidation in the kidney. It also decreases FA synthesis in the kidney and the liver and these processes could prevent lipid accumulation and, in consequence, the release of significant amounts of FA into the bloodstream. Besides, curcumin decreases CD36 in the kidney and the liver (5/6Nx group), which diminishes FA uptake and lipogenesis in the liver. This could prevent lipoprotein (VLDL) formation in the liver, which was reflected in its bloodstream concentrations that were decreased by curcumin. Thus, curcumin improves mitochondrial function, preventing lipid accumulation in the kidney, liver, and bloodstream and avoiding oxidative stress and tissue injury. The figure was created using BioRender.