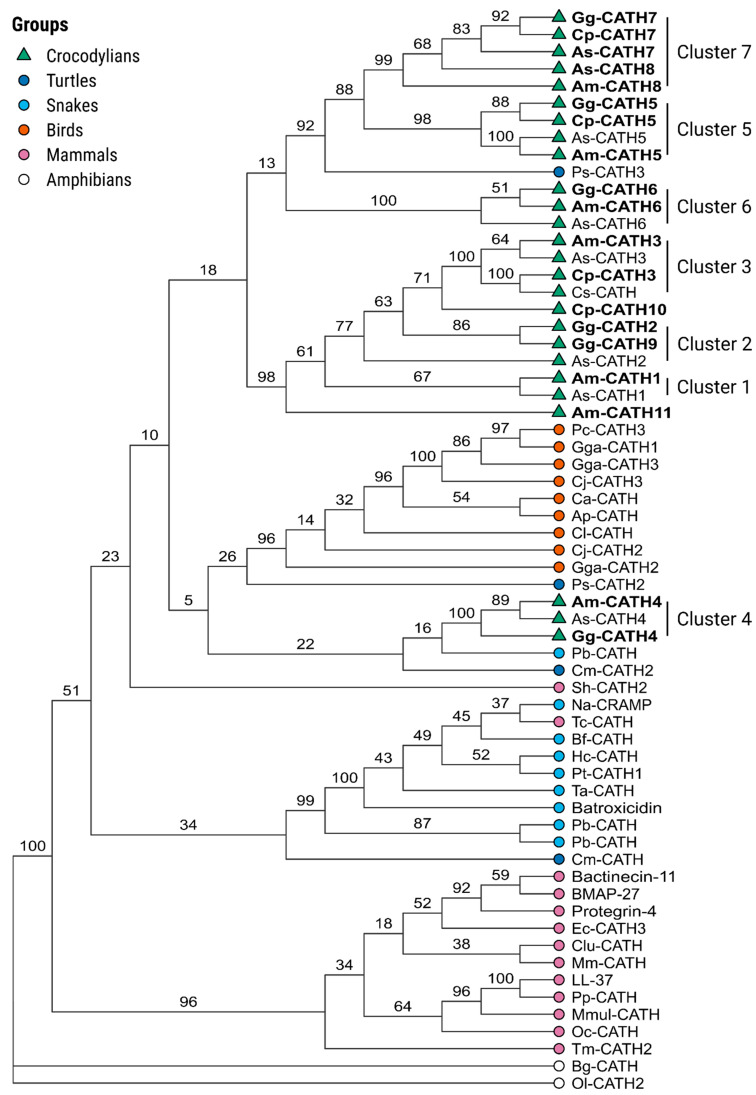
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of crocCATH sequences. The tree was generated using the maximum likelihood criterion implemented in the RaxML program. The analysis included the full-length crocodylian amino acid sequences, as well as sequences from other reptilian, avian and mammalian species. Newly identified crocCATH sequences are displayed in bold. The amphibian cathelicidins Bg-CATH and Ol-CATH2 were used as outgroups to root the tree. Branch numbers indicate statistical support as percent after 1000 bootstrap replicates. The seven identified crocodylian clusters are indicated in the figure, which were named according to the previously described A. sinensis cathelicidins [18]. The alligator cathelicidin AM-36 [19] was renamed here as Am-CATH4. NCBI accession numbers of all cathelicidin sequences can be found in Supplementary Tables S1 and S3.