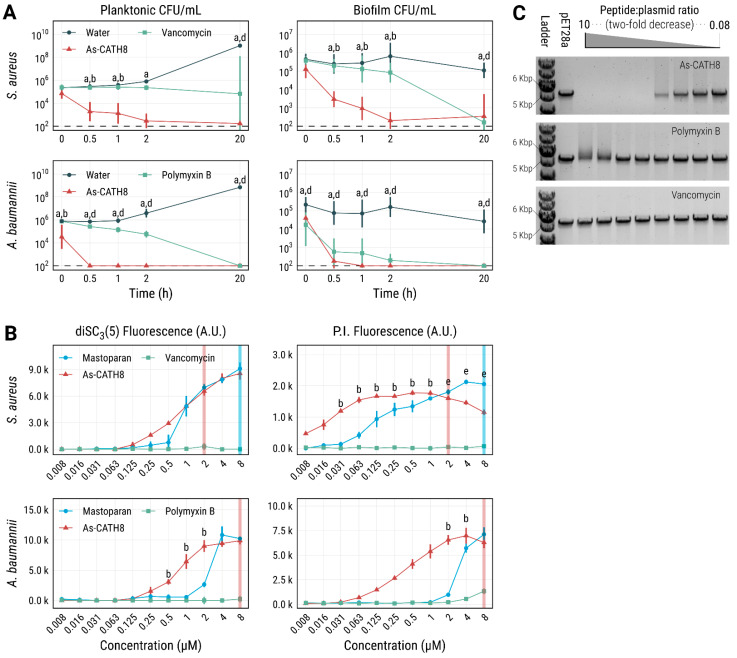
Figure 4.
Bacterial killing rate, membrane depolarization and permeabilization and DNA binding capacity of As-CATH8. (A) Killing of planktonic S. aureus and A. baumannii cells at the MIC in MHB media. Antibiofilm activity was assessed in 10% TSB supplemented with 0.1% glucose at 64-fold MIC. CFU data are displayed as geometric mean ×/geometric standard deviation. (B) Cytoplasmic membrane depolarization and permeabilization were assessed after 1 h treatment of planktonic cells using DiSC3(5) and PI, respectively. Membrane-permeabilizing wasp peptide mastoparan was used as a positive control. Shown are fluorescence readings (mean ± standard error in arbitrary units). Perpendicular lines represent the minimal peptide concentration leading to at least 1000-fold CFU reduction compared to the untreated control (see also Supplementary Figure S4). (C) Gel electrophoretic mobility shift assay demonstrating the DNA binding capacity of As-CATH8, employing the linearized plasmid pET28a at 2-fold decreasing peptide:plasmid weight ratios (see Supplementary Figure S5 for an uncropped image). Peptidic antibiotics vancomycin (active against S. aureus) and polymyxin B (active against A. baumannii) were used as comparisons. Letters denote statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between As-CATH8 and water (a), As-CATH8 and antibiotics (b), As-CATH8 and mastoparan (c), antibiotics and water (d) or antibiotics and Mastoparan (e) according to the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc test with the Benjamini–Hochberg p-value correction. All experiments were performed at least three times independently.