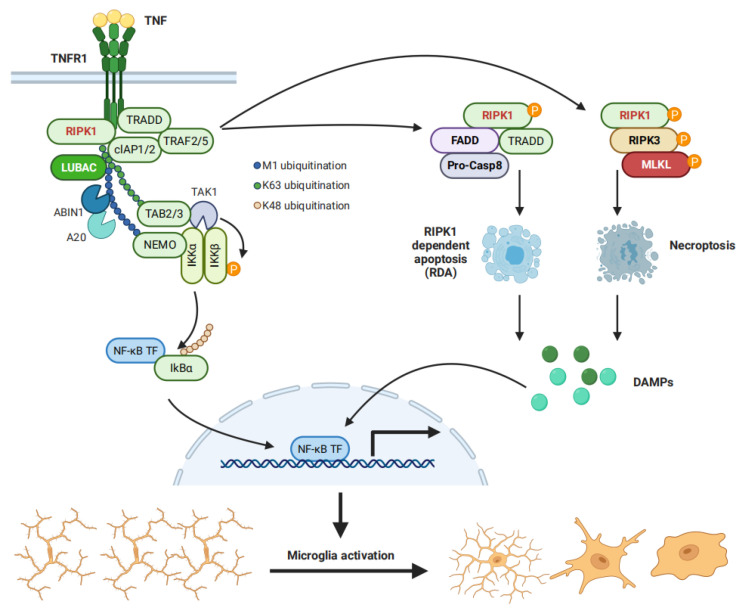
Figure 1.
TNFR1 activation promotes NF-κB activation via cell-autonomous and non-autonomous mechanisms. TNF binds to TNFR1 to form an intracellular protein complex that promotes the activation of NF-κB via the scaffold function of RIPK1 (Left). The kinase activity of RIPK1 mediates RIPK1-dependent apoptosis (RDA) when cFLIPL expression induced by NF-κB is comprised, while activated RIPK1 promotes necroptosis when active caspases are inhibited (Right). Both RDA and necroptosis cause the release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) to activate the NF-κB pathway via non-cell autonomous mechanisms.