Figure 5. Cell-type-dependent requirements of essential enhancers.
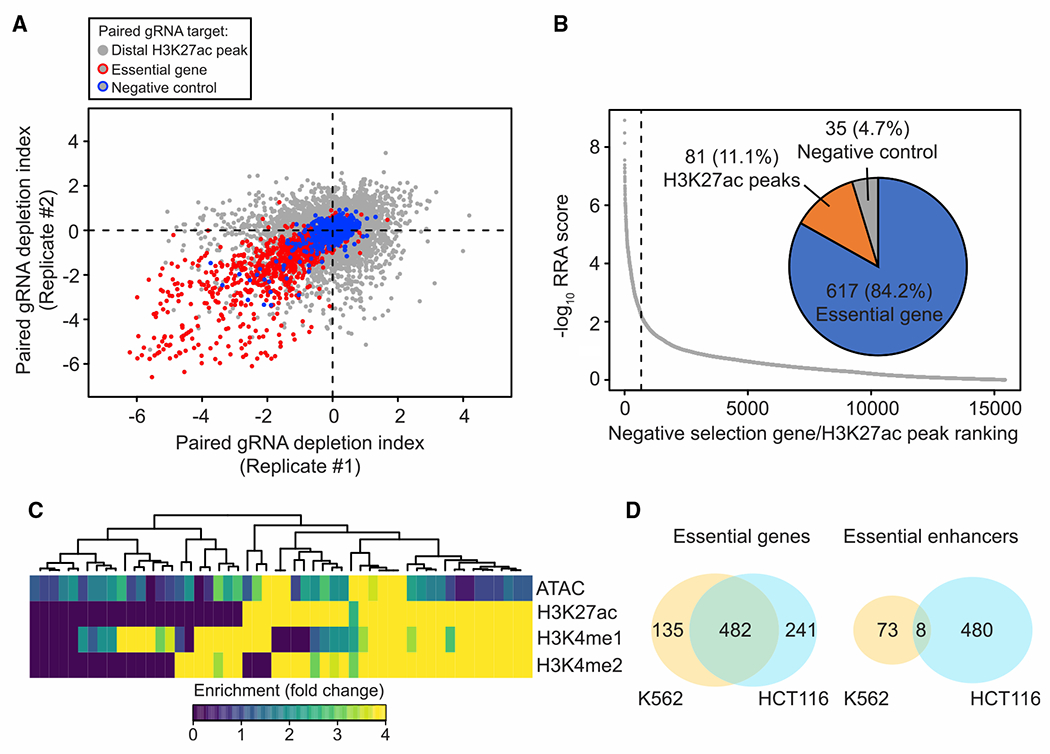
(A) Correlation of fitness effects in two biological replicates from CRISPRi screen in K562 (Pearson’s R = 0.51). Red circled dots indicate pgRNAs targeting the promoter of essential genes and blue circled dots indicate pgRNAs targeting the promoter of the non-expressed genes. Gray dots represent pgRNAs targeting distal H3K27ac peaks selected from HCT116.
(B) Summary of candidate targets identified from the K562 screen. Target with a smaller RRA score (identified by the MAGeCK algorithm) indicates a more substantial reduction in proliferation screen. Overall, 617 of the significant targets are essential genes, while 81 are distal H3K27ac peaks, and 35 are non-expressed genes or safe targets from negative control groups.
(C) Heatmap showing chromatin state of essential enhancers identified from K562. Each row represents the signal from the indicated dataset and each column represents individual essential enhancers identified in K562 cells.
(D) Venn diagram showing the number of overlapped essential genes (left) and essential enhancers (right) identified from K562 and HCT116 cells (yellow, K562; cyan, HCT116).
