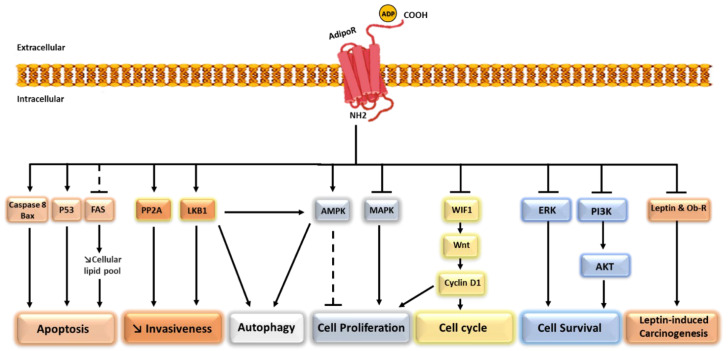
Figure 1.
Potent anti-cancer activities of adiponectin by modulating a wide range of signaling pathways. Adiponectin binds to AdipoR1/2 and (1) inhibits cell proliferation by activating AMKP and inhibiting MAKP, (2) induces cell cycle arrest by indirect inhibition of Cyclin D1 through the Wnt pathway, (3) inhibits invasiveness by activating LKB1 and PP2A, (4) induces apoptosis by activating Bax, Caspase 8, and P53 and decreasing the cellular lipid pool through the inhibition of FAS, (5) induces autophagy through LKB1 and AMKP, (6) decreases cell survival through the inhibition of ERK and PI3K, and finally, (7) inhibits leptin-induced carcinogenesis by decreasing the expression of Leptin and the Leptin receptor. ADP: Adiponectin, Bax: Bcl-2–associated X, FAS: Fatty acid synthase, PP2A: Protein phosphatase 2A, LKB1: Liver kinase B1, AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase, MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase, WIF1: Wnt inhibitory factor-1, Wnt: Wingless-related integration site, ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase, PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Akt: Protein kinase B, Ob-R: Leptin receptor.