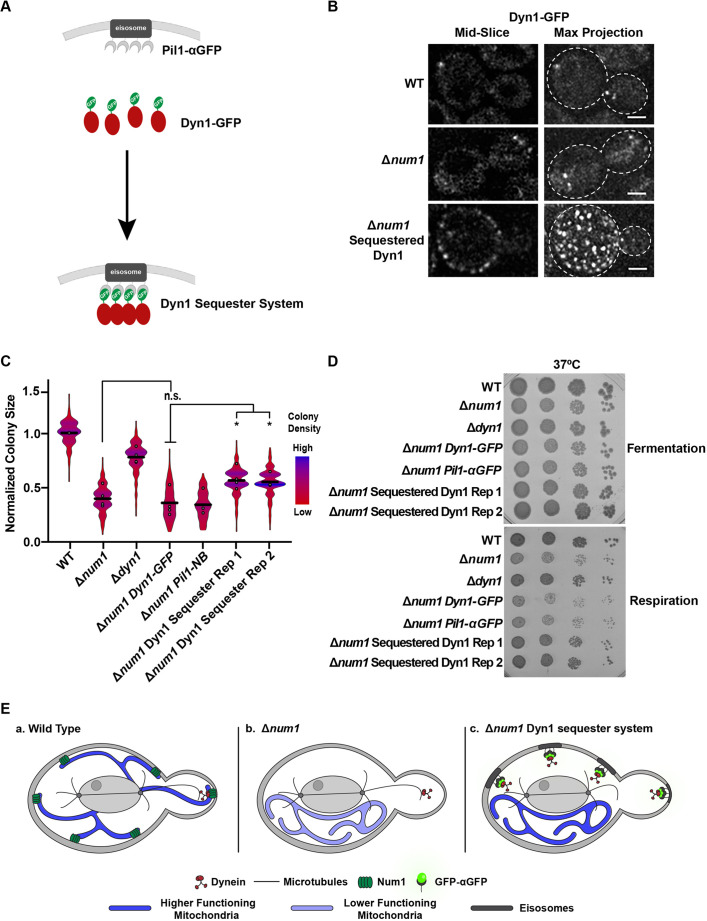
Fig. 6.
Artificially sequestering dynein at the cell cortex rescues the respiratory growth defect of Δnum1 cells. (A) Schematic depicting the GFP–αGFP nanobody system used to artificially sequester Dyn1–GFP at the PM. (B) WT, Δnum1 and Δnum1 Pil1-αGFP cells expressing Dyn1–GFP were grown in fermentative growth conditions and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Whole-cell, maximum intensity projections and a single focal plane from the middle of the cell are shown. Dashed white lines denote the outline of the cell. Scale bars: 2 µm. (C) Quantification, presented as a violin plot, of WT, Δnum1, Δdyn1, Δnum1 DYN1-GFP, Δnum1 Pil1-NB and Δnum1 Dyn1 Sequester cell growth at 35°C in respiratory growth conditions as described in Fig. 1E. Black line denotes the grand mean of at least four independent experiments and the circles depict the mean of each independent experiment; n≥399 colonies per strain. Rep 1 and Rep 2 denote two independent isolates of Δnum1 Sequestered Dyn1. The fold change in colony size between a Δnum1 DYN1-GFP and Dyn1 Sequester Rep 1 and Rep 2 is 1.3 and 1.2, respectively, which is similar to rescue observed in Fig. 5C. (D) To supplement the colony size assays shown in Fig. 6C, serial dilutions of the indicated strains were spotted onto YPD (fermentative growth condition) or YPEG (respiratory growth condition) agar plates and grown at 37°C. Images shown in B and D are representative of two and three repeats, respectively. (E) In WT cells (a), Num1 serves as a cortical anchor for dynein. The loss of Num1-mediated dynein anchoring at the cortex results (b) in reduced mitochondrial function by a yet-to-be-described mechanism that depends on the ability of dynein to directly associate with microtubules. Artificially sequestering the dynein complex at the PM in Δnum1 cells restores mitochondrial function (c), supporting the idea that the reduced mitochondrial function in Δnum1 cells is a consequence of unanchored dynein. *P≤0.05; n.s., not significant (two-tailed unpaired t-test).