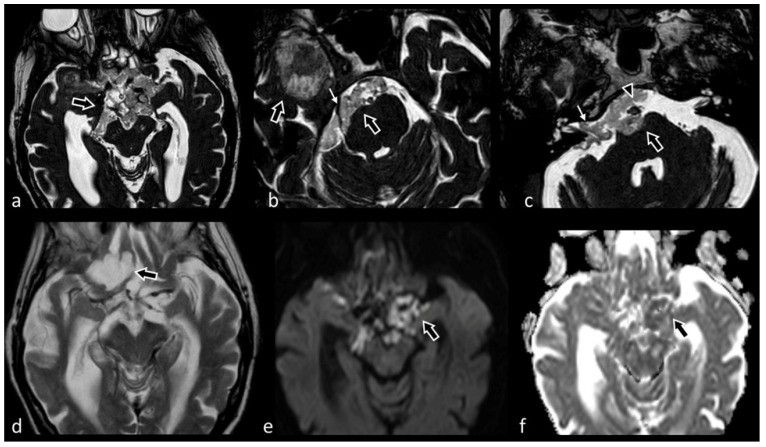
Figure 11.
Voluminous extra-axial lesion centered in the suprasellar cistern, diffusively extending into the contiguous cisternal spaces as well as into Sylvian and choroid fissures bilaterally; inferiorly, the mass also runs along the prepontine cistern, the Meckel’s cave and the internal auditory canal (small white arrow in (c). The lesion appears isointense to CSF in T2-TSE (d), markedly hyperintense on DWI (e) and partially and lightly hypointense on ADC maps (f). 3D CISS (a–c) is superior compared to the other sequences in demonstrating the internal texture of the lesions, its margins as well as its relation with surrounding structures (e.g., fifth cranial nerve, small white arrow in (b), and basilar artery, arrowhead in (c), which are encased but not dislocated by the mass). These features, alongside the characteristic hyperintensity in DWI, are highly suggestive for an epidermoid cyst.