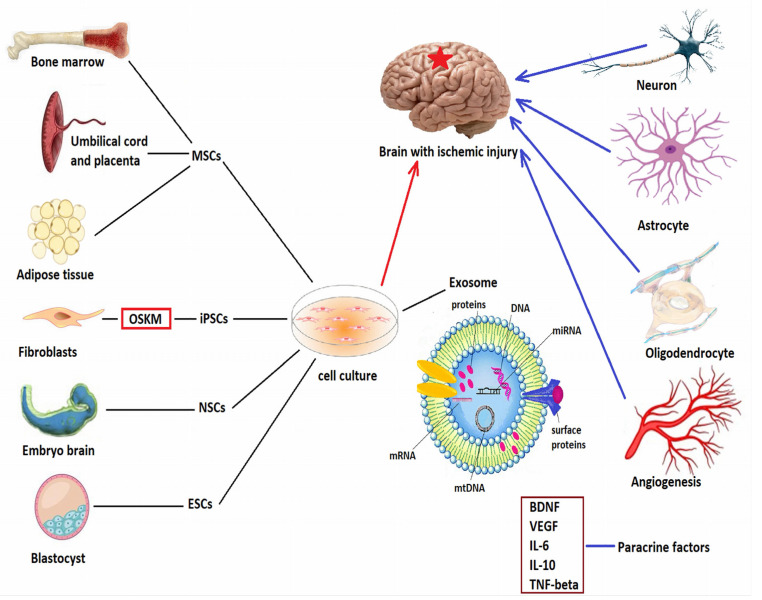
Figure 2.
Embryonic pluripotent stem cells (ESCs) are derived from the inner layer of the blastocyst, Neural multipotent stem cells are obtained from human fetal cortex, mesencephalon, or spinal cord. Mesenchymal multipotent stem cells can be harvested from bone marrow, umbilical cord and placenta, or from adipose tissue. There is also the possibility of obtaining induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) via transduction of the four OSKM genes: octamer-binding transcription factor 4 (Oct4), sex-determining region Y-box 2, (Sox2), the Krupellike factor 4 (Klf4), and the avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog (c-myc). Once harvested, stem cells are cultured in special culture medium, where they release exosomes carrying proteins, DNA, messenger RNA (mRNA), microRNAs (miRNA), and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Once delivered to the brain by various routes, they differentiate into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes, and release various growth factors (such as brain derived neurotrophic factor-BDNF or vascular endothelial growth factor-VEGF) and anti-inflammatory cytokines (interleukins IL-6, IL-10, or tumor necrosis factor β), which modulate neuroinflammation and promote angiogenesis, neurogenesis, neural differentiation, and synaptogenesis.