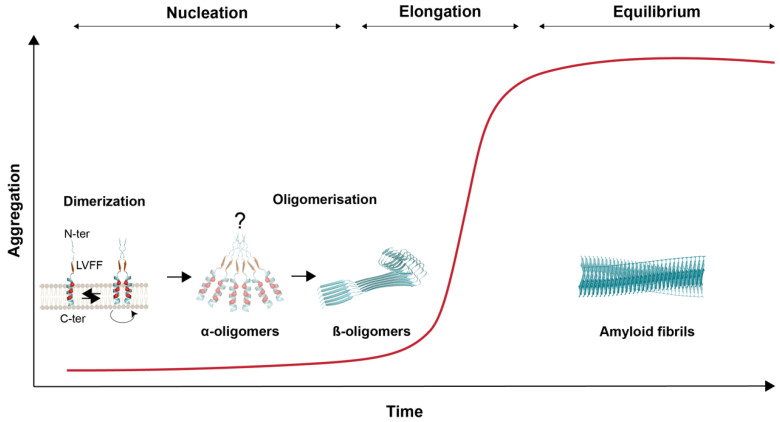
Figure 5.
Steps of amyloid β aggregation. Illustration of putative nucleation steps of Aβ adapted from [152]. γ-secretase cleaves monomers of C99 (see above) but released Aβ peptides may rapidly reform dimers centered on the GxxxG motifs. In the nucleation phase, dimer formation is the initial step leading to the formation of higher-order species (hexamers are represented) whose nucleation is mediated by the Aβ C-terminus. These oligomers usually form β-sheets but may go through a transient step to form α-oligomers that rapidly switch to more stable β-oligomers initiated by the LVFF motif. Elongation occurs by assembly of β-sheet oligomers into fibrils.