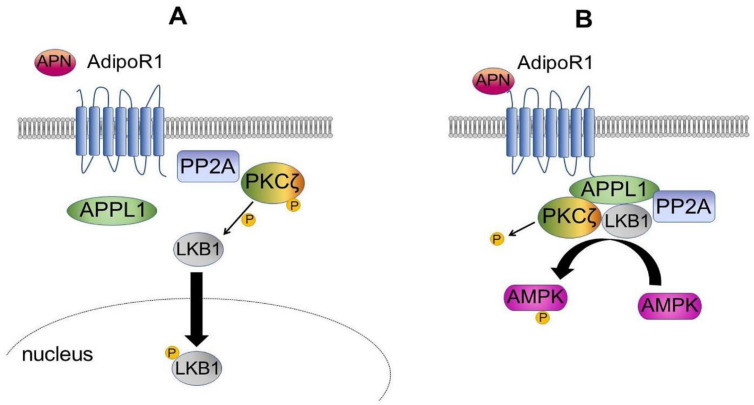
Figure 4.
PVAT control vascular function by mean of precise mechanism related to adiponectin-dependent AMPK activation. Two conditions are relevant. (A) non-stimulated with no link between adiponectin (APN) and Adiponectin receptor 1 (AdipoR1). Adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interacting with PH domain and leucine zipper 1 (APPL1) do not work alongside protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). Protein kinase Cζ (PKCζ) induces phosphorylation of liver kinase B 1 (LKB1) affecting its translocation to the nucleus. (B) The stimulated state induces the bind of APN to AdipoR1 with activation of APPL1 resulting in PKCζ dephosphorylation by P. Dephosphorylated PKCζ is no longer effective to phosphorylate LKB1. PP2A also dephosphorylates LKB1, which results in LKB1 translocation to the cytoplasm. LKB1 phosphorylates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in the form of the AdipoR1/APPL1/PP2A/ PKCζ/LKB1 complex. Abbreviations are in the text.