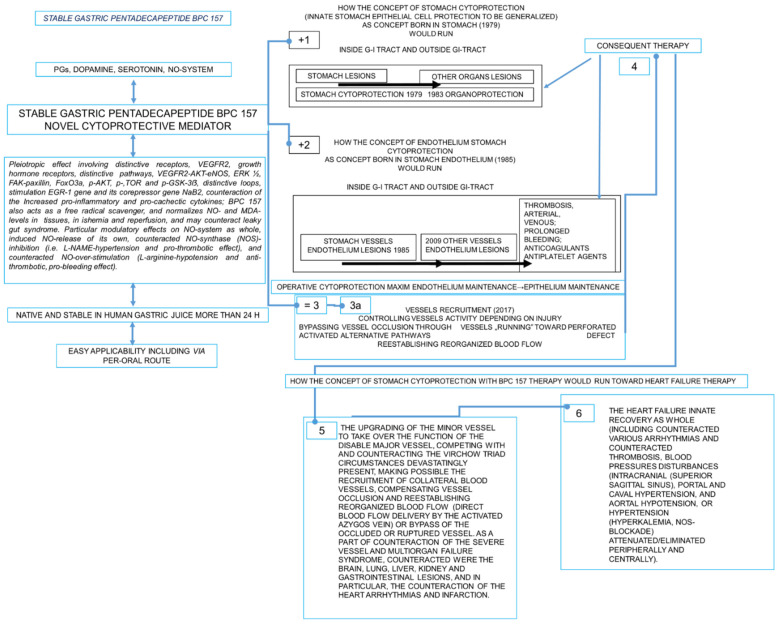
Figure 1.
Description of the BPC 157 therapy. Cytoprotection concept (for review, see [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]) born in the stomach appears with cytoprotective agents application as innate stomach epithelial cell protection (indicated as +1) to be generalized (Robert, Szabo) in other organs epithelia protection (organoprotection) supplemented by stomach endothelium cell protection (indicated as +2) (Szabo). Together (+1, +2), these result in cytoprotection stomach maxim endothelial maintenance→epithelial maintenance (indicated as = 3) as axis for the rapid defensive response to resolve the ongoing lesions, which is, however, not fully operative with the standard cytoprotective agents. As novel cytoprotection mediator, BPC 157 might exert prominent epithelial beneficial effects in the stomach and in the whole gastrointestinal tract and in the other organs (stomach cytoprotection→organoprotection) (+1) and endothelial beneficial effect in the stomach (+2). Therefore, BPC 157 therapy might make the stomach maxim endothelial maintenance→epithelial maintenance (indicated as =3) a fully operative axis (indicated as 3a). Further, BPC 157 therapy might extend the original cytoprotection maxim endothelial maintenance→epithelial maintenance from the stomach to the other vessels endothelium protection (3a) [18,19,24,27,29,31,37,38,39,40,41]. In this, BPC 157 might induce particular vessel recruitment and activation depending on injury, i.e., when confronted with vessel occlusion, there was collateral activation to bypass vessel occlusion, as well as when confronted with perforated defect, vessel “running“ toward the defect (3a) [18,19,24,27,29,31,37,38,39,40,41]. The rapid result is the re-establishing of the reorganized blood flow (3a). As consequence, there was a particular therapy that might beneficially affect thrombosis, arterial and venous, and lesions presentation (indicated as 4). For the BPC 157 therapy of the heart failure, BPC 157 therapy might induce particular upgrading of the minor vessel to take over function of the disabled major vessel, resolving Virchow triad circumstances devastatingly present, making possible collateral vessels activation, compensating function of the major vessel, reestablishing reorganized blood flow (direct blood flow by the activated azygos vein) (indicated as 5) [18,19,24,27,29,31,37,38,39,40,41]. In confrontation with the severe syndrome (i.e., heart failure, in particular), the successful activation of the compensatory collateral circulation was ascribed to the counteraction of the vascular and multiorgan failure, counteraction of the intracranial (superior sagittal sinus), portal and caval hypertension and aortal hypotension (5) [18,19,24,27,29,31,37,38,39,40,41]. The final result of the BPC 157 therapy (indicated as 6) might be the heart failure innate recovery as a whole (including counteracted various arrhythmias and counteracted thrombosis, blood pressures disturbances (intracranial (superior sagittal sinus), portal and caval hypertension, and aortal hypotension [19,24,27,29,31,37,38,39,40,84], or hypertension (hyperkalemia, NOS-blockade) [62,67] attenuated/eliminated peripherally and centrally). Moreover, as part of the general beneficial pleiotropic effect (as part of the cytoprotection background) [2,3,4,5,6,7,8], there was the counteraction of the concomitant severe vessel and multiorgan failure syndrome [19,24,27,29,31,37,38,39,40], the counteraction of the brain, lung, liver, kidney and gastrointestinal severe lesions, almost annihilated thrombosis, counteraction of the escalated general peripheral and central syndrome. In addition, BPC 157 also acts as a free radical scavenger, counteracts free radical-induced lesions, and normalizes NO and MDA levels in tissues and during ischemia and reperfusion [5,6,19,22,24,25,27,28,29,30,32,33,34,38,39,90,160,161], and thereby, due to its particular cytoprotective/cardioprotective activity [2,3,4,5,6,7,8], it might beneficially affect the myocardial lesions, in particular [19,24,27,29,31,37,38,39,40,41,84]. Finally, in addition to the clear demonstration of the therapeutic efficacy in the most adequate animal models as proof of the concept, the additional evidence involves particular interaction with many molecular pathways [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,20,22,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57]. Pleiotropic effects involving distinctive receptors, including VEGFR2 and growth hormone receptors, distinctive pathways, including VEGFR2-AKT-eNOS, ERK ½, FAK-paxillin, FoxO3a, p-AKT, p-mTOR and p-GSK-3β, and distinctive loops, including stimulation of the egr-1 gene and its corepressor gene naB2, and counteraction of increases in pro-inflammatory and procachectic cytokines, and counteraction of the leaky gut syndrome [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,20,22,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57], likely minimize the inherent lack of full understanding of the mechanisms that may be involved. In the interaction with many molecular pathways [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,20,22,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57], particular consideration should be given to the evidence of the BPC 157/ NO-system’s particular importance (i.e., the endothelium and thrombocytes function both maintained (for review, see, i.e., [2,3,4,5,6,7,8])). BPC 157 therapy counteracted thrombocytopenia in rats that underwent major vessel occlusion and deep vein thrombosis [22] and counteracted thrombosis in all vascular studies [18,19,23,24,27,28,29,31,37,38,39,40]), and coagulation pathways not affected [58,59,60]. Further arguments might be controlling vasomotor tone and the activation of the Src-Caveolin-1-eNOS pathway [53,54]. This likely occurred as the particular modulatory effects on NO-system as a whole, induced NO-release of its own [61,62,63], counteracted NOS-inhibition [61] (i.e., N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methylester (L-NAME)-hypertension and pro-thrombotic effect) [58,62], and counteracted NO-over-stimulation [61] (L-arginine-hypotension and anti-thrombotic, pro-bleeding effect) [58,62]. Likewise, the isoprenaline-myocardial infarction was counteracted as NO-effect [38]. Thus, due to its close interaction with NO-system as NO acts as an endogenous cardioprotectant antifibrillatory factor [64,65] and BPC 157 might have a particular therapeutic effect.