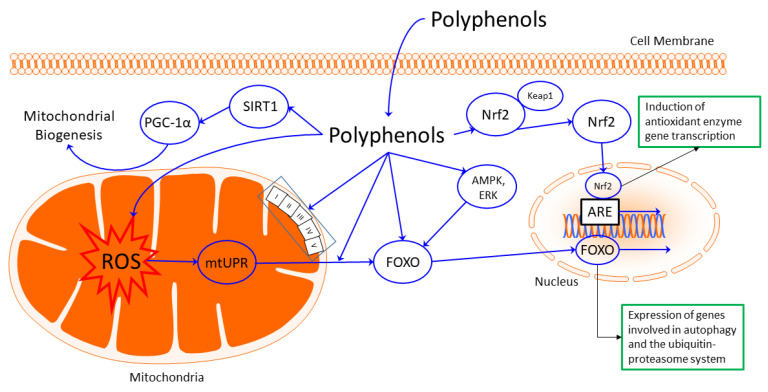
Figure 1.
Possible interactions between polyphenols and metabolic pathways associated with aging. After biotransformation, polyphenols may acquire the ability to cross the cell membrane into the cytosol. It is in the cytosol that the polyphenols exert their effects. Mitochondrial biogenesis is stimulated by polyphenols via an SIRT1-activated PGC-1α-mediated mechanism. Mitochondrial stress triggered by ROS production in the mitochondria can be averted either directly or indirectly by ROS scavenging or by the influence of polyphenols on FOXO transcription factor activation. Polyphenols cause the dissociation of Keap1 from the Nrf2/Keap1 complex. Translocation of Nrf2 to the nucleus leads to its association with ARE in the regulatory regions of target genes. This process induces the transcription of antioxidant and detoxification enzymes. Some polyphenols can directly affect oxidative phosphorylation or complexes of ETC. In this way, energy performance can be changed.