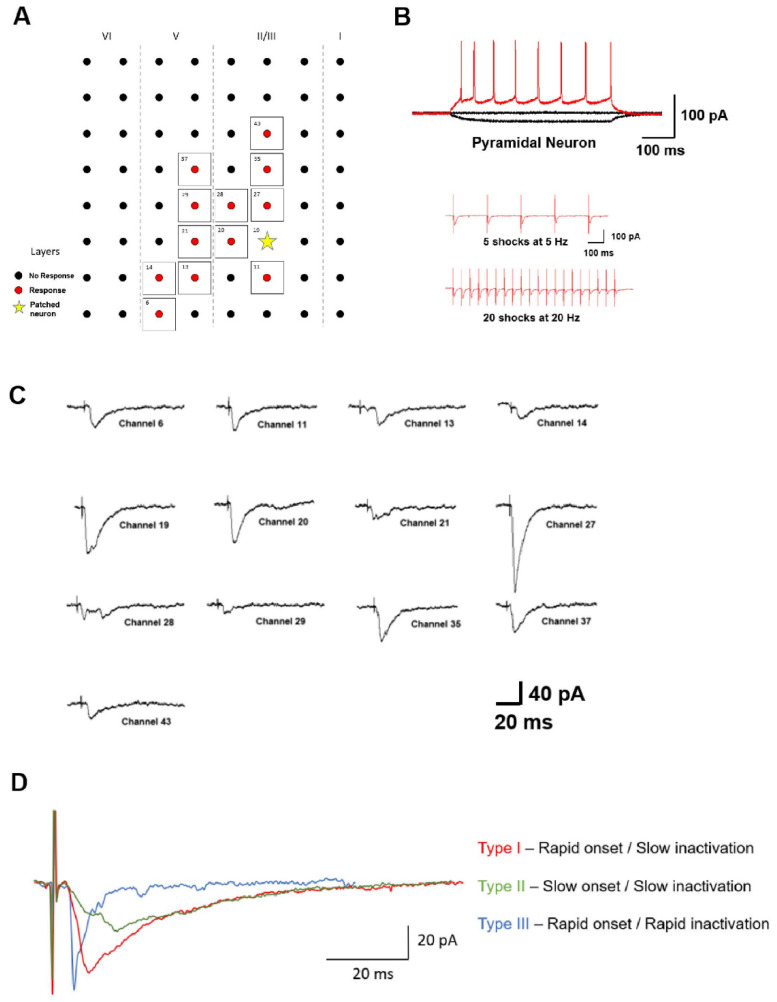
Figure 2.
ACC pyramidal neurons receive heterogeneous inputs: (A) A representative mapping of a neuronal network within the ACC. The yellow star represents the patched neuron, while the red dots represent channels that elicit a response in the patched neuron when stimulated. Representative traces (right) of the responses recorded in the patched neuron when stimulations were given to different channels. (B) Identification of pyramidal type by injecting step currents (−50, 0, and 50 pA). Monosynaptic connectivity was tested using 5 shocks at 5 Hz and 20 shocks at 20 Hz. Responses triggered without failure in the presence of picrotoxin (100 µM) indicate monosynaptic connectivity. (C) Sample traces from the recorded neuron show responses with different characteristics. (D) Three representative traces are depicted to illustrate the three different types of response kinetics that were observed: Type 1—Rapid onset followed by a slow inactivation phase illustrated in red, Type II—Slow onset followed by a slow inactivation phase illustrated in green, and Type III—Rapid onset followed by rapid inactivation illustrated in blue. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [44] 2021, Jung-Hyun Alex Lee.