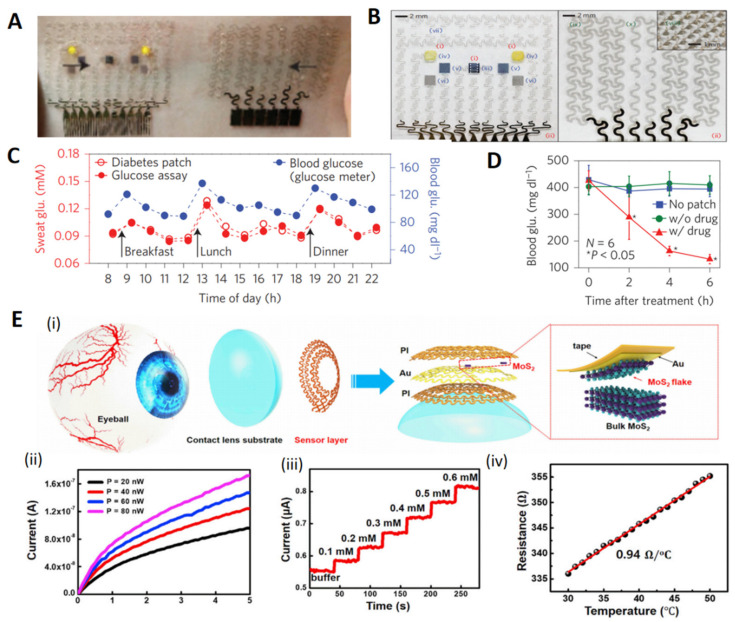
Figure 5.
Several highly integrated wearable sensors based on 2D materials. (A): Optical camera images of the diabetes patch laminated on human skin. (B): Schematic diagram of a GP-hybrid electrochemical unit consisting of electrochemically active and soft functional material (xi), gold-doped graphene (xii), and serpentine gold mesh (xiii) from top to bottom. (C): One-day monitoring of human sweat and blood glucose concentrations in human sweat and blood. (D): Comparison of blood glucose concentrations in db/db mice in the treatment group (with drug) and control group (without patch and without drug) when used on diabetic mice [128]. Copyright 2018, Springer Nature. (E): (i) Schematic diagram of the different layers of the smart contact lens structure attached to the eye. The dashed area highlights the gold-mediated mechanical peeling of a single layer of MoS2. (ii) Leakage source characteristics of the photodetector at different light intensities. (iii) Time vs. current curves based on changes in glucose levels. (iv) Resistance versus strain of the temperature sensor at different temperatures [129]. Copyright 2020, Elsevier.