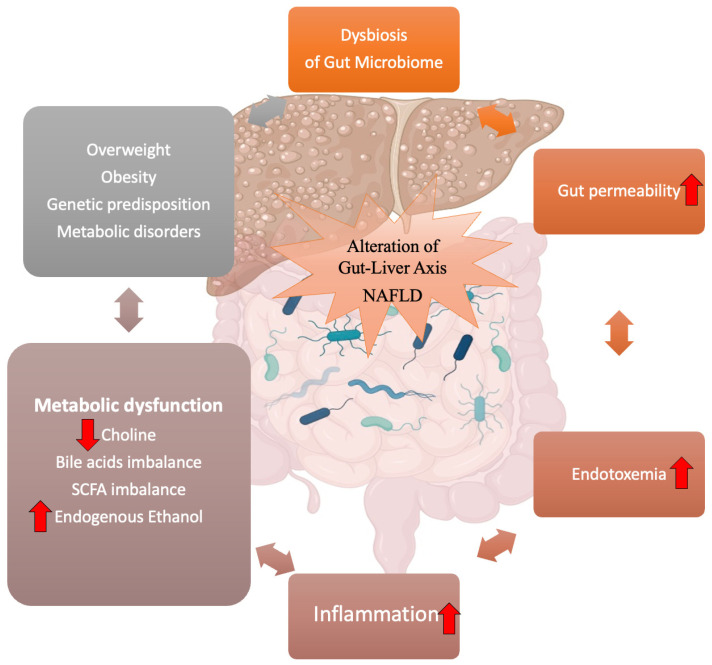
Figure 1.
Gut–liver axis and NAFLD: a vicious circle of dysfunctions orchestrated by the gut microbiome. Alteration of the gut–liver axis is characterized by several pathological mechanisms, such as the impairment of the gut barrier and consequent increase of the intestinal permeability which result in endotoxemia and inflammation, and changes in bile acid profiles and metabolite levels (increasing of endogenous ethanol, reduction of choline levels, dysregulation of SCFA metabolism) produced by the gut microbiome. Gut microbiome dysbiosis has a prominent role in the disruption of the gut–liver axis. Created with https://BioRender.com (accessed on 10 October 2022) and modified with Microsoft PowerPoint v.16. SCFA: short-chain fatty acid; NAFLD: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.