Figure 3.
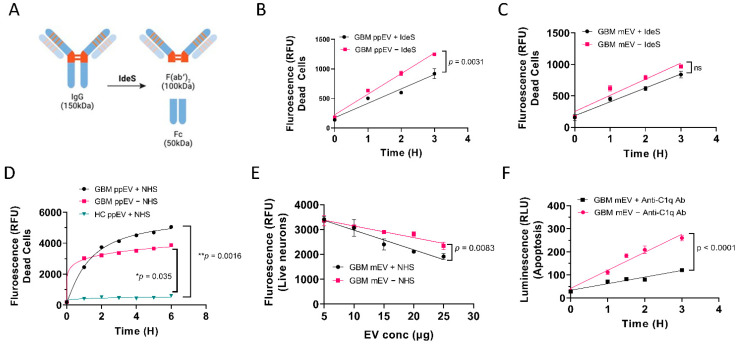
Reduced levels of GBM EV-induced neuronal cytotoxicity were observed by IgG digestion and complement elimination. (A). Schematic drawing showing digestion of IgG with the highly specific IgG cleaving enzyme IdeS. B-C. Reduced levels of cell death were observed in SH-SY5Y cells with IdeS-digested GBM EVs. GBM EVs were digested with IdeS before incubating with cells. (B). Significantly lower levels of cytotoxicity were found in cells treated with IdeS digested GBM pooled plasma EVs (ppEV) compared to undigested EVs (p = 0.0031). (C). Although not significant, a similar trend was seen when treating cells with IdeS digested GBM cell line medium-derived EVs (mEV) compared to undigested EVs. (D). Normal human serum (NHS) enhanced GBM plasma EVs induced cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. GBM ppEVs (5 µg/well) were added to cells with or without 5% NHS and the cytotoxicity was measured by green-fluorescent necrosis dye. NHS increased GBM ppEV cytotoxicity when compared to GBM ppEV treatment without NHS. However, without NHS, GBM ppEVs nonetheless induced elevated cytotoxicity compared to HC ppEVs. (E). Live cell counts post EV treatment. Human primary neurons were treated with GBM mEVs with or without 5% NHS. The cytotoxicity was measured using the live/dead assay (1 µM Calcein AM/2 µM Ethidium Homodimer1). Increasing GBM EV concentration produced fewer live cells, and NHS treatment enhanced the GBM EV cytotoxicity compared to samples without NHS (p = 0.0083). (F). Blocking of complement component C1q with anti-C1q antibody inhibits GBM EV-induced apoptosis. Rabbit anti-C1q antibodies (4 µg/well) were incubated with cells during GBM EV treatment. C1q antibody produced significantly lower levels of apoptosis in a time-dependent manner (p < 0.0001).