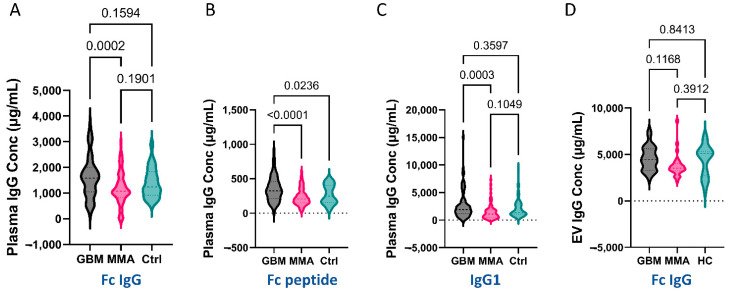
Figure 4.
Higher levels of IgG antibodies were detected in GBM plasma with a similar trend in GBM plasma EVs. For plasma ELISA, a total of 82 GBM, 83 MMA, and 50 control plasmas were used. (A,B). Significantly higher levels of total Fc IgG antibodies were detected in GBM plasma. The 96-well MaxiSorp ELISA plates were coated with capture antibodies (10 µg/mL goat anti-human IgG Fc antibody, (A), or 100 µg/mL of synthetic Fc-III-peptide (B) overnight at 4 °C. Fc IgG antibodies in diluted plasma were detected by biotinylated goat anti-human IgG (H + L) antibody followed by the addition of NeutrAvidin-HRP and TMB. (A). Higher Fc-IgG antibodies were detected in GBM plasma compared to MMA plasma (p = 0.0002). (B). GBM plasma had significantly higher levels of Fc-IgG captured by Fc peptides compared to both MMA (p < 0.0001) and controls (p = 0.02). (C). Higher levels of IgG1 in GBM plasma compared to MMA. Mouse anti-human IgG1 antibodies were coated on ELISA plates overnight followed by the addition of plasma (1:2000). Biotinylated goat anti-human IgG-Fc antibody and NeutrAvidin-HRP were used for detection. IgG1 levels in GBM plasma were significantly higher compared to MMA plasma (p = 0.0003), but not significantly different to controls. (D). No significant difference was detected in the Fc IgG levels among GBM, MMA, and HC EVs (GBM = 26, MMA = 26, HC = 20).