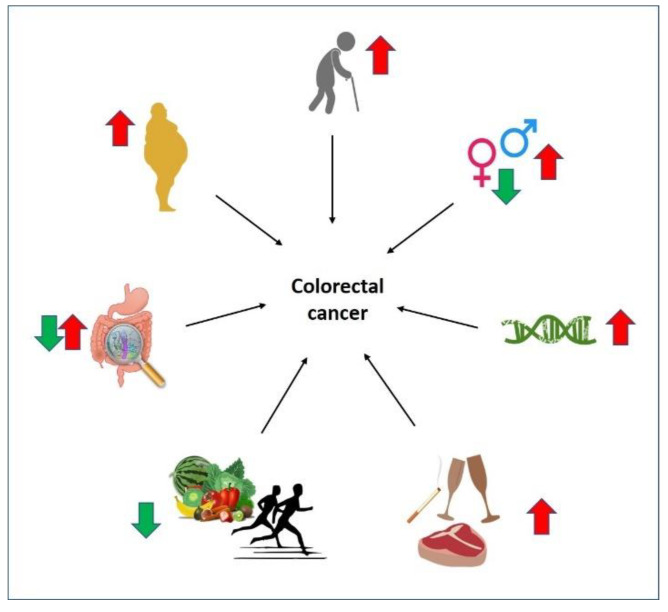
Figure 1.
Factors influencing CRC risk. Factors influencing CRC risk are indicated by arrows where a red arrow indicates high risk while a green arrow low risk of developing CRC. (1) Elderly people are at high risk of CRC development; (2) compared to males, females have a lower risk of developing CRC due to the protective effect of estrogen. However, CRC development risk is increased in females over 65 years of age compared to males of similar age; (3) molecular changes such as CIN, MSI, and CIMP as well as families with a strong history of CRC increase the risk of developing CRC; (4) lifestyle of high consumption of alcohol, heavy smoking, and consumption of red meat and processed red meat amplifies CRC risk; (5) on the other hand, regular exercise and dietary habit of including fruits and vegetables that have high fibers have been reported to reduce CRC risk; (6) alteration of the gut microbiome can affect the CRC risk in both directions; (7) disease such as obesity has been strongly related to CRC development; moreover, obese males are at higher risk of developing CRC than obese females as females have the local estrogen production by adipose tissue.