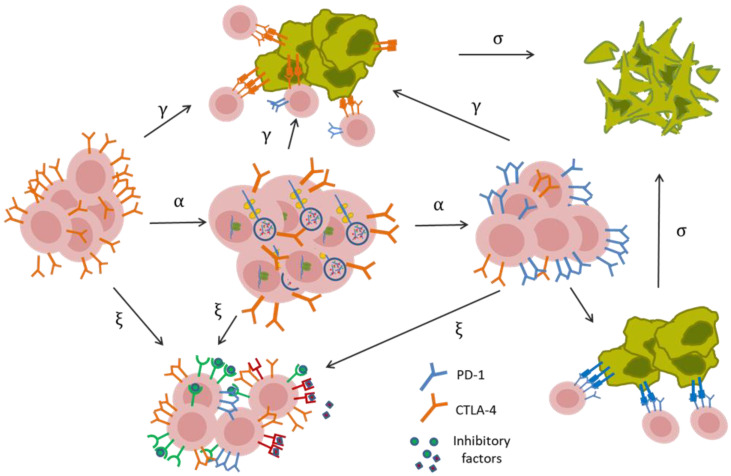
Figure 2.
Illustration of the relationships between the components of the mathematical model. PD-1 and CTLA-4 receptors and other factors suppress lymphocyte activity in the tumor microenvironment. As a result of the cytoplasmic storage of preformed CTLA-4 molecules, the total population of active lymphocytes can express the CTLA-4 receptor with no time delay and can be potentially inactivated by this receptor at a gamma rate. Other inhibitory factors can also suppress lymphocytes, independent of PD-1 receptor signaling. The regulation of PD-1 expression occurs mainly at the genetic and epigenetic levels, resulting in a time delay in immune suppression triggered by PD-1 receptors. Concurrently, the cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes results in the death of tumor cells.