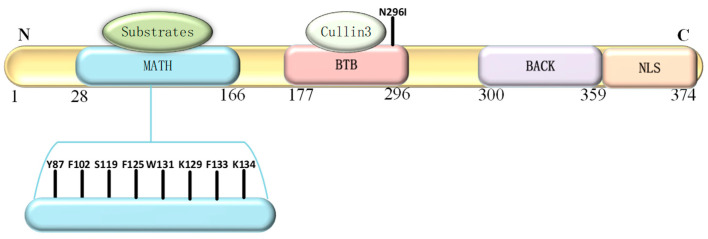
Figure 1.
Illustration of the structural features of Speckle-type POZ (pox virus and zinc finger protein) protein (SPOP). The modular structural arrangement of SPOP is shown, which includes the N-terminal meprin and TRAF homology (MATH) domain that selectively recognizes and recruits substrates. Somatic mutations are predominantly clustered in several key amino acids in the N-terminal MATH domain, including Y87, F102, S119, F125, K129, W131, F133 and K134. The Bric-a-brac-Tramtrack/Broad (BTB) domain is responsible for binding to cullin3 and SPOP dimerization, which also involves the BACK domain. The nuclear localization signal (NLS) is a C-terminal nuclear localization sequence.