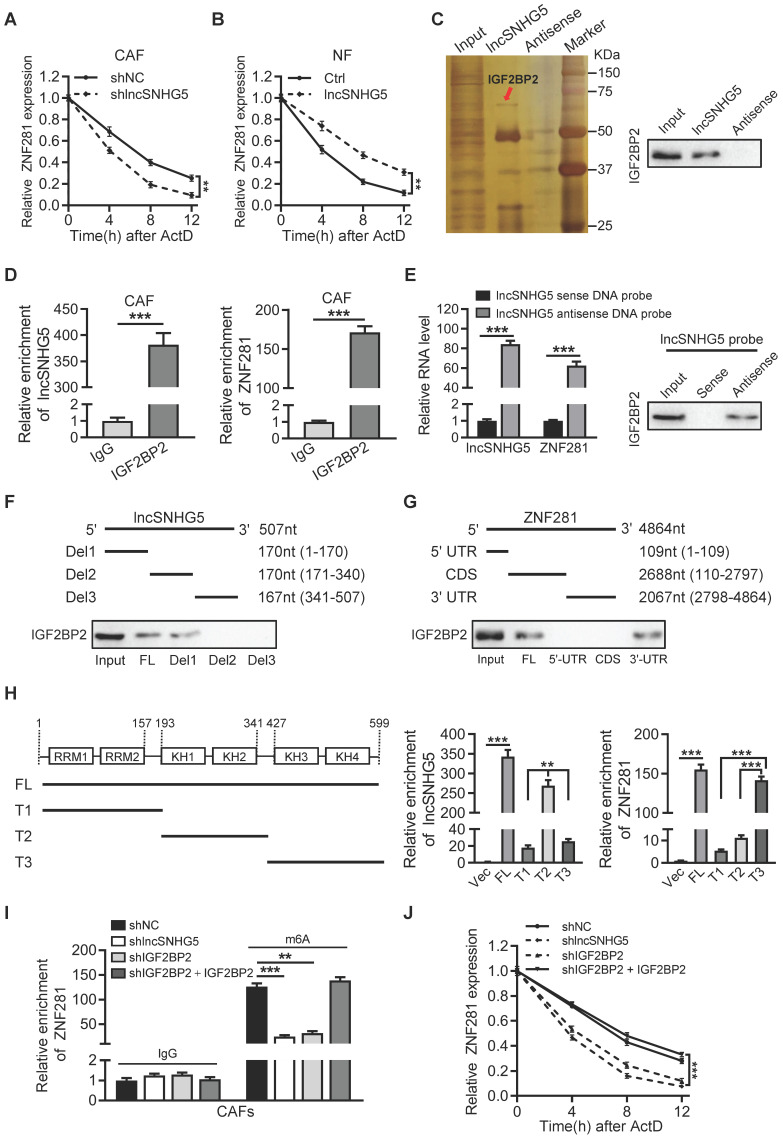
Figure 4.
lncSNHG5 binding with the m6A reader IGF2BP2 enhances the mRNA stability of ZNF281. (A-B) qRT-PCR was used to determine ZNF281 mRNA levels in lncSNHG5-knockdown CAFs (A), lncSNHG5-overexpressing NFs (B) and their control cells following actinomycin D treatment at the designated time. (C) RNA pull-down was conducted with antisense and sense lncSNHG5 in CAF lysates, followed by silver staining and western blotting. An obviously changed band of IGF2BP2 is shown. (D) RIP assay for CAF lysates was performed using anti-IGF2BP2 and anti-IgG, and the enrichment of lncSNHG5 and ZNF281 in the RIP precipitates was determined by qRT-PCR. (E) RNA pull-down was performed with antisense or sense lncSNHG5 biotinylated DNA probe in CAF lysates, and the RNA levels of lncSNHG5 and ZNF281 and IGF2BP2 proteins in the pull-down precipitates were measured by qRT-PCR and western blotting, respectively. (F, G) Western blotting to examine IGF2BP2 in the pull-down precipitates with biotinylated full-length or segmented lncSNHG5 (F) or ZNF281 (G) probes in CAFs. (H) The lncSNHG5 and ZNF281 binding domains in IGF2BP2 were identified using full-length or truncated IGF2BP2 by RIP-qPCR. (I) The m6A-modified ZNF281 mRNA levels in the indicated CAF lysates were determined using a gene-specific m6A qPCR assay. (J) qRT-PCR to verify the relative mRNA expression of ZNF281 in the indicated CAFs treated with actinomycin. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).