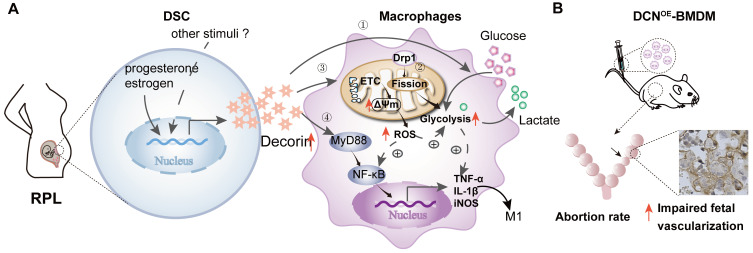
Figure 10.
DCN promotes decidual M1-like macrophage polarization via mitochondrial dysfunction resulting in the occurrence of RPL. (A) Aberrant high levels of DCN, which is secreted by DSCs and induced by progesterone and estrogen, lead to the dysfunction of decidual macrophages in the decidua of women with RPL. Dysfunction of decidual macrophages is characterized by an increasing proportion of M1-like macrophages, accompanied by TNFα and IL-1β production. Notably, this polarization to M1-like macrophages is related to increasing mitochondrial membrane potential and glycolysis, promoting mitochondrial fission mediated by DRP1, enhancing ROS production, and activating the MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway. (B) Transfer of DCN-treated BMDMs increases the mouse embryo absorption during early pregnancy, accompanied by impaired fetal vascularization.