Figure 1. Fabrication and characterization of polony gels.
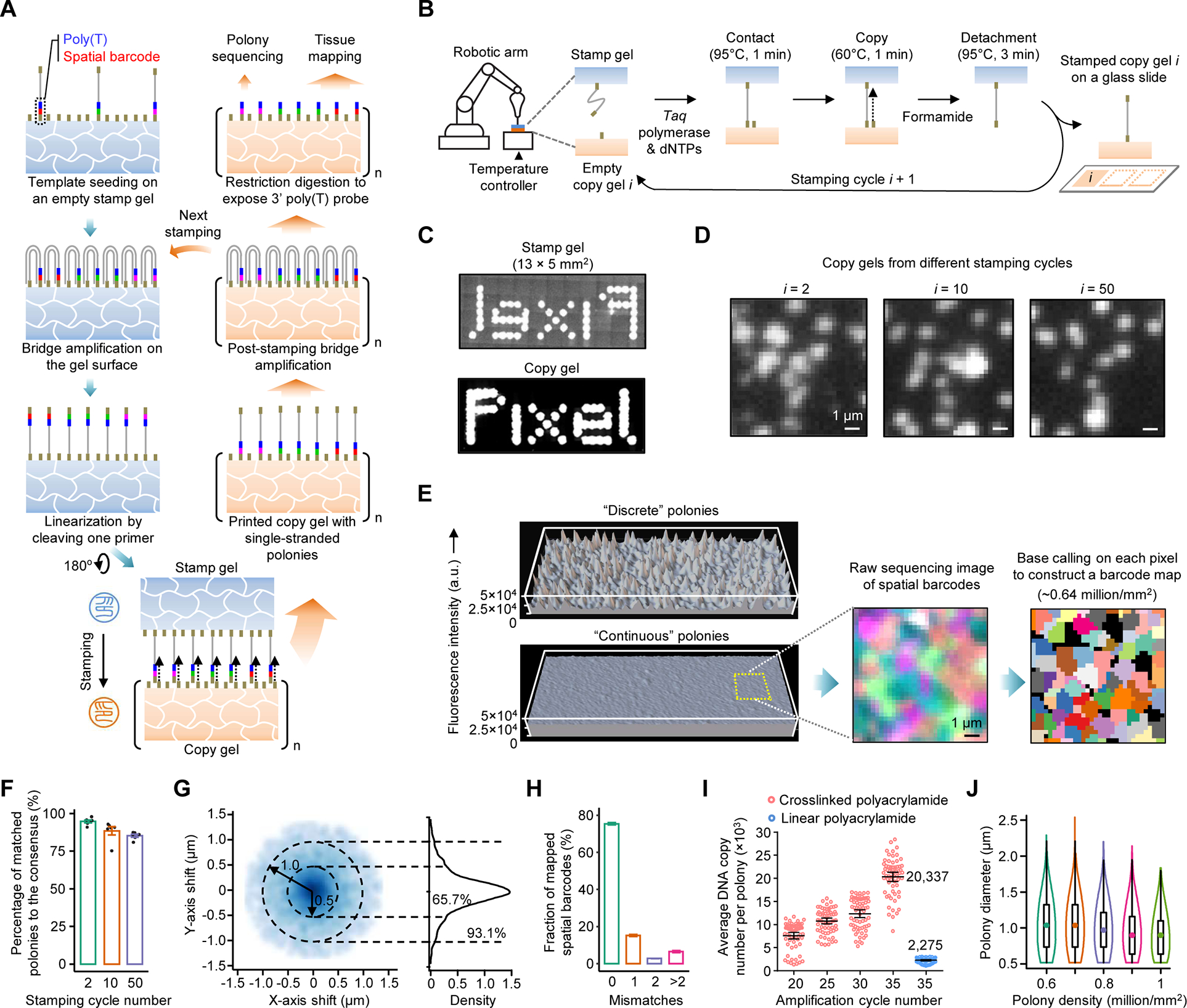
(A) Schematic of the amplifiable DNA stamping. USER-linearized single-stranded polonies are copied from a stamp to many copy gels. Copied DNAs are further bridge amplified to complete the replication. A few copy gels are used as the stamp for next fabrication or for polony sequencing to create a spatial barcode map; the majority are used for tissue mapping assays.
(B) A gel-to-gel DNA copying process automated with a stamping device.
(C) Millimeter-scale images of SYBR Green-stained polonies in a stamp and a copy gels. For comparison, templates were seeded on the masked, ~40-μm-thick stamp gel and amplified to polonies showing a pattern of the word “Pixel”.
(D) Images of SYBR Green-stained polonies from the 2nd, 10th, and 50th stamping cycles. The low-density polony gels (~105/mm2) were selected to facilitate visual comparison.
(E) 3D intensity profiles of SYBR Green-stained, discrete and continuous polonies amplified from templates seeded at the same density by 35 cycles.
(F) Four-channel sequencing images of two high-density polony gels (~8 × 105/mm2) from the 2nd and 10th stamping cycles. A spatial barcode map was generated by the pixel-level base calling.
(G) Box plot of the percentages of polonies in copy gels matched the consensus. Data represent means of six sampled gel positions each found with 195 to 332 polonies; error bars, standard deviation.
(H) 2D and 1D density plots of relative positions of polony centers in copy gels from the consensus. Dash circles denote center drifts of 0.5 and 1 μm. n = 4,521 and 11,441 for polonies at the low and high densities, respectively.
(I) Box plot of barcode error rates in eluted DNAs from two copy gels detected by Illumina sequencing.
(J) Comparison of polony bridge amplification efficiencies for two gel substrates. The linear polyacrylamide coating was prepared by a reported Illumina method.
(K) Violin plot of measured diameters of polonies at different densities. n = ~0.6 to 1 million.
