Fig. 2. Context-specific GENRE analysis of C. difficile CD196 reveals significant metabolic shifts when in coculture with Enterococcus.
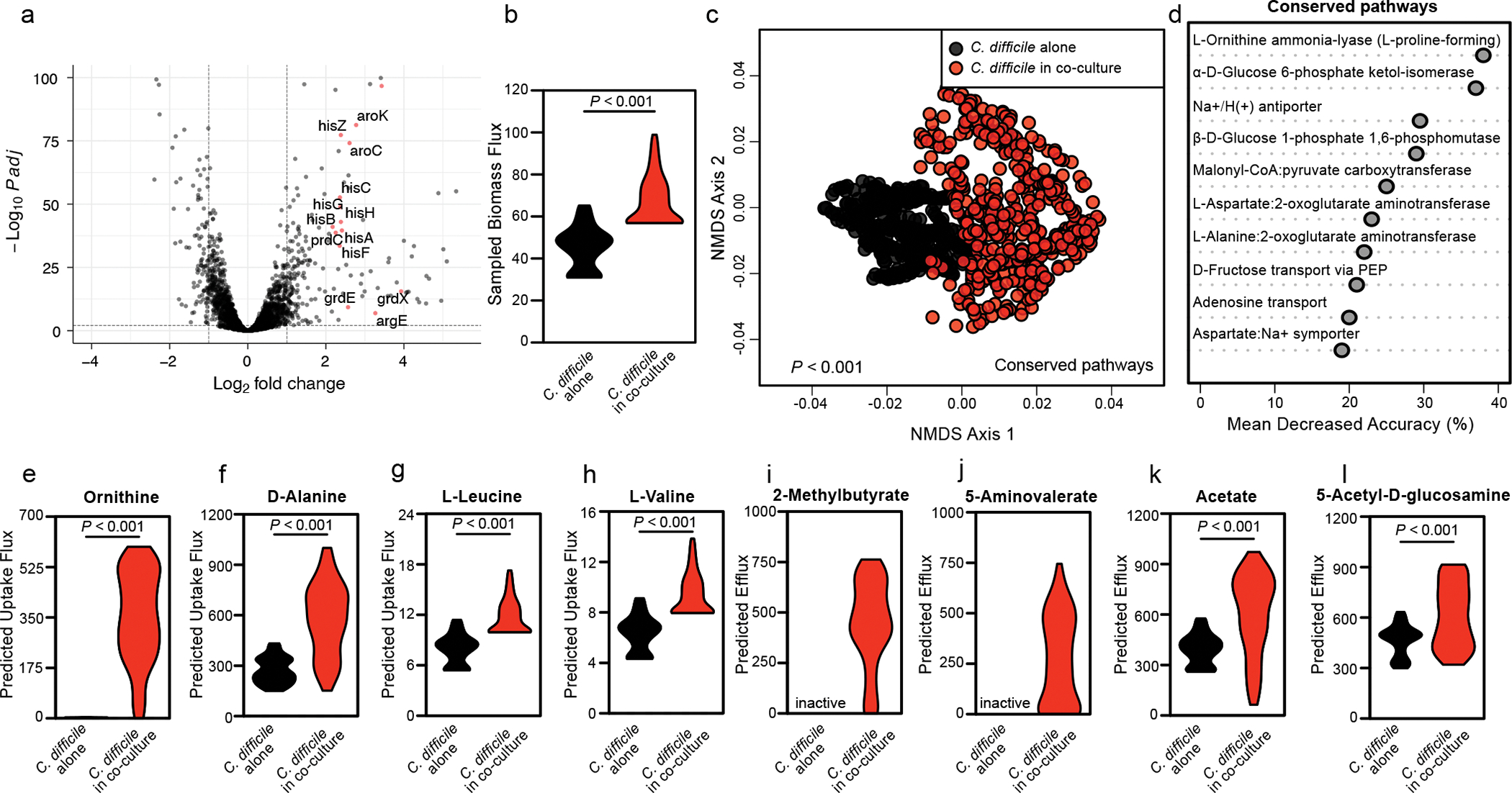
(a) Volcano plot showing C. difficile transcripts altered following co-culture measured by RNA sequencing. Significance determined using two-sided Wald test and corrected for multiple comparisons using the Benjamini-Hochberg method. Red points denote genes associated with amino acid metabolism. (b) Samples of metabolic flux states with biomass synthesis as the objective function in each context-specific model. Significant difference calculated by two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test (P<0.001). (c) Non-metric Multidimensional Scaling of Bray-Curtis dissimilarities for flux samples of all shared reactions across both experimental contexts. Significant difference determined by one-way PERMANOVA (P=0.001). (d) AUC-Random Forest supervised machine learning results highlighting reactions that differentiate flux distributions during C. difficile growth and C. difficile growth in the context of E. faecalis (k = 10; OOB = 0%). (e-h) Difference in simulated uptake of (e) L-ornithine (P<0.001), (f) D-alanine (P<0.001), (g) L-leucine (P<0.001), or (h) L-valine (P<0.001) across context-specific models. (i-l) Difference in (i) 2-methylbutyrate, (j) 5-aminovalerate, (k) acetate (P<0.001), and (l) N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (P<0.001) efflux across context-specific models. Significance determined by two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
