Figure 14.
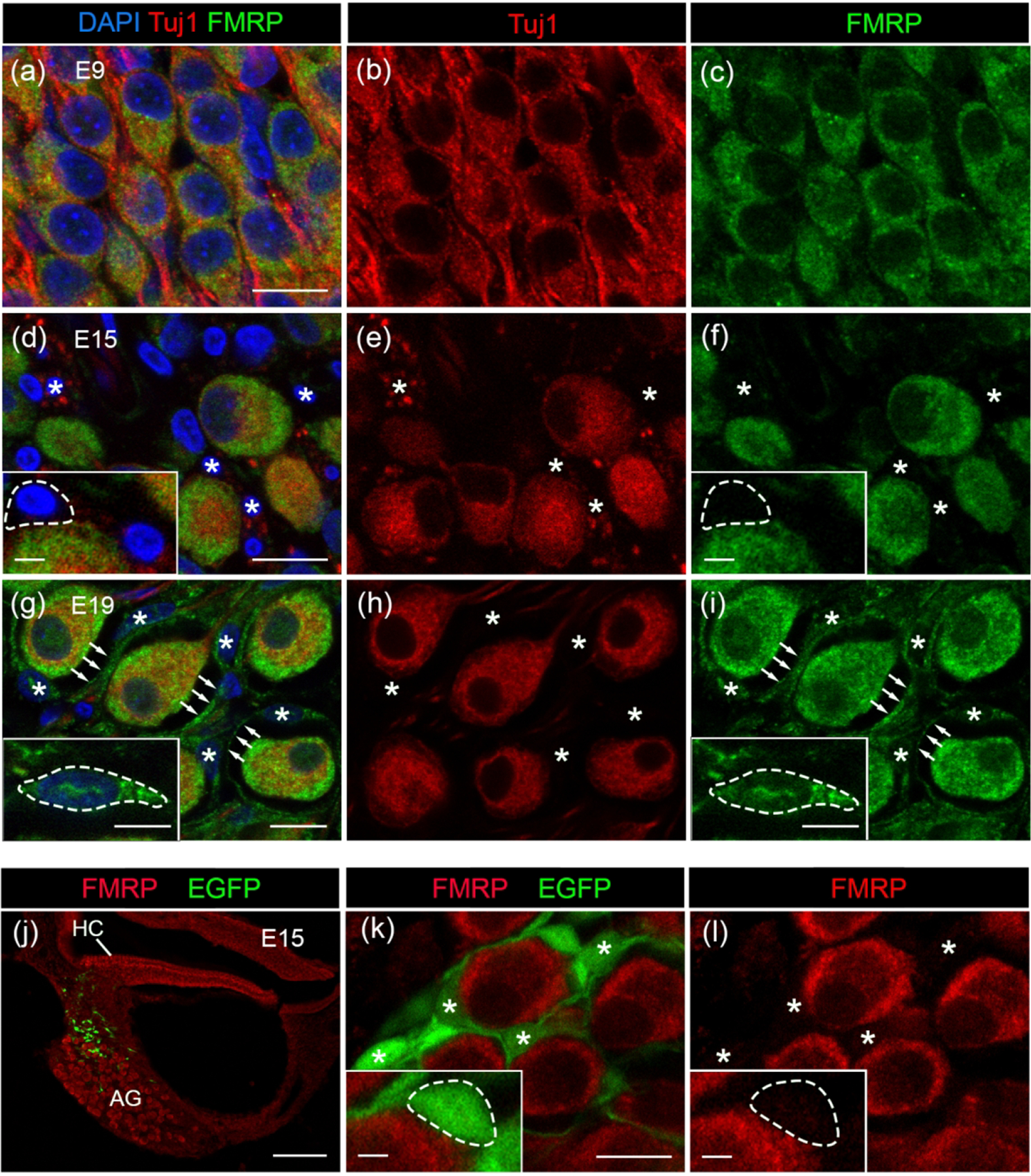
FMRP_PA8263 immunostaining in the chicken satellite glial cells during development. (a–i) FMRP (green) and Tuj1 (red) double immunostaining on cochlea cross sections counterstained with DAPI (blue) at E9 (a–c), E15 (d–f), and E19 (g–i). Asterisks indicate the location of glial cell bodies. Arrows point along the FMRP-immunoreactive envelops surrounding AG neurons. Insets in d, f, g, and I show enlarged glial cell bodies with dashed outline. (j–l) PA8263 immunoreactivity (red) on cochlea cross sections from a E15 chicken embryo that was transfected with EGFP (green) via in ovo electroporation of scrambled Fmr1 shRNA-EGFP constructs (Wang et al., 2018). (j) and (k–l) are low- and high-magnification images of AG, respectively. AG neurons are surrounded by EGFP-positive glial cells and their processes, which contained no or little FMRP. Asterisks indicate the cell bodies of transfected satellite glial cells. Insets in k and l show enlarged glial cell soma with dashed outline. Scale bars = 10 μm in a, applies to a–c; 10 μm in d, applies to d–f; 10 μm in g, applies to g–i; 10 μm in k, applies to k–l; 100 μm in j; 2 μm in insets of d, f, k, l; 5 μm in insets of g, i.
