Figure 15.
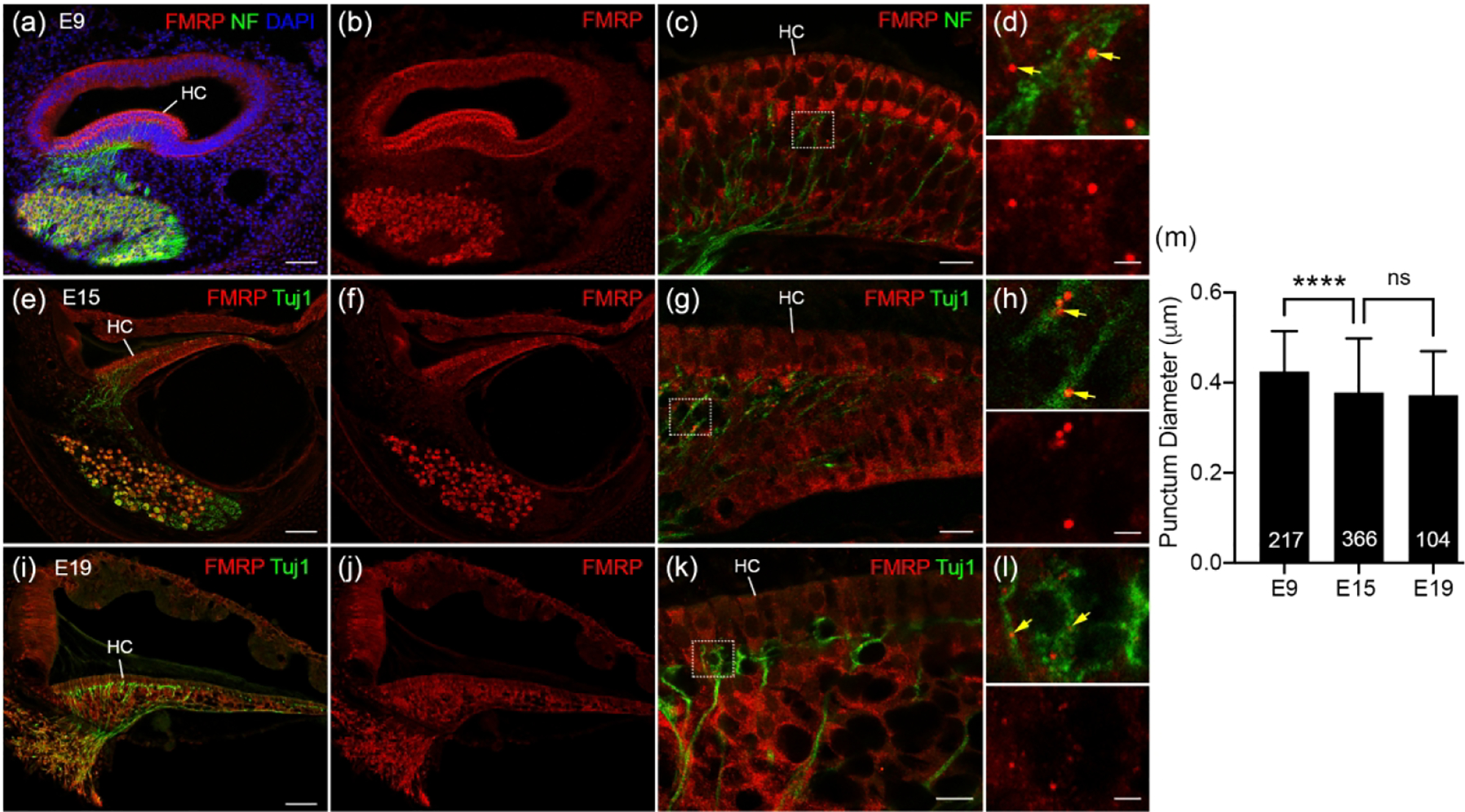
FMRP_PA8263 immunostaining in the distal peripheral processes of chicken auditory ganglion (AG) during development. (a-b) Low-magnification images of FMRP (red) and Neurofilament (NF, green) double immunostaining on E9 cochlea cross section counterstained with DAPI (blue). (c) High-magnification of FMRP and NF immunostaining in the E9 BP. (d) Closer view of the box in c. Yellow arrows point to FMRP puncta located in NF-labeled processes. (e–f) Low-magnification of FMRP (red) and Tuj1 (green) double immunostaining in E15 cochlea. (g) High-magnification of FMRP and Tuj1 immunostaining in the E15 BP. (h) Closer view of the box in g. Yellow arrows point to FMRP puncta located in Tuj1-labeled processes. (i–j) Low-magnification images of FMRP (red) and Tuj1 (green) double staining in E19 cochlea. (k) High-magnification images of FMRP and Tuj1 immunostaining in the E19 BP. (l) Closer view of the box in k. Yellow arrows point to FMRP puncta located in Tuj1-labeled processes. (m) Quantification of FMRP punctum size. The punctum diameter is 0.42 ± 0.09 μm at E9, 0.38 ± 0.12 μm at E15, and 0.37± 0.10 μm at E19. One-way ANOVA was performed followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons: F (2, 684) = 14.70. ****p<0.0001; ns, not significant. Scale bars = 50 μm in a, applies to a–b; 50 μm in e, applies to e–f; 50 μm in i, applies to i–j; 10 μm in c, g, k; 2 μm in d, h, l.
