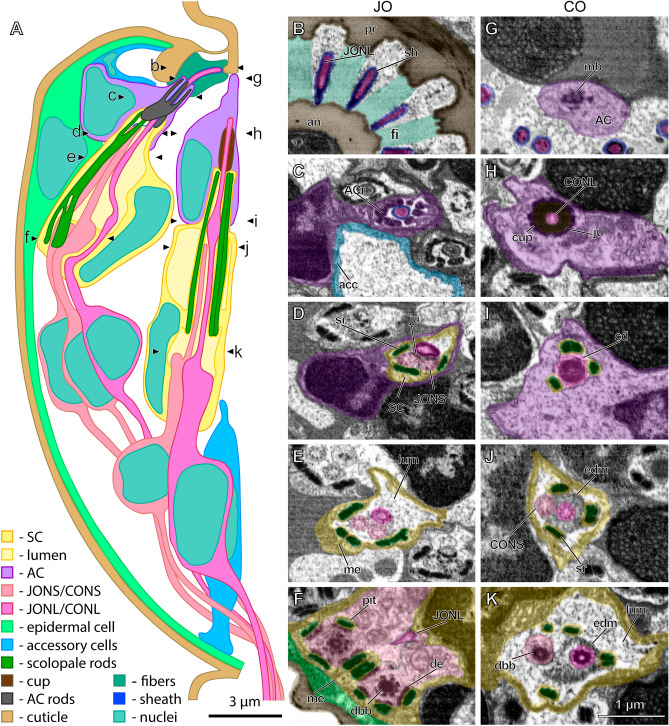
Figure 1.
Ultrastructure of pedicellar chordotonal organs in Megaphragma viggianii. (A) Scheme of longitudinal section of M. viggianii pedicel with one Johnston’s organ (JO) and one central organ (CO) scolopidia. Letters designate the approximate location of cross sections shown in B–K. (B–F): Cross sections of JO scolopidium (FIB-SEM). (B) A sheath covers the tips of long JO neurons (JONL) cilia that lie between the fibers connecting pedicel rim and annelus. (C) Attachment cell (AC) forms a thin channel containing JONL cilium tip. Accessory cell surrounds a cavity filled with granular material. (D) Projections of scolopale cell (SC) containing scolopale rods surround JO cilia tips connected with junctions. (E) JO cilia lie in a lumen surrounded by SC that forms mesaxon. (F) Bulbs of short JO neurons (JONS) dendrites are joined by desmosomes to the scolopale rods, one rod is inserted in a small pit. (G–K): Cross sections of CO scolopidium (FIB-SEM). (G) A bundle of microtubules is observed in AC. (H) Tip of long CO neuron (CONL) cilium fits inside of a cap joined to the AC by junctions. (I) Four scolopale rods form a triangle around the cilium dilation of CONL. (J) A band of electron-dense material lies below the cilium dilation. (K) Distal basal bodies lie in CONL and short CO neuron (CONS) Cilia surrounded by electron-dense material. (acc—accessory cell, ACr—AC rods, an—annelus, cd—cilium dilation, dbb—distal basal body, de—desmosome, edm—electron-dense material, fi—fiber, ju—junction, lum—lumen, mb—microtubule bundle, me—mesaxon, pr—pedicel rim, sh—sheath, sr—scolopale rod).