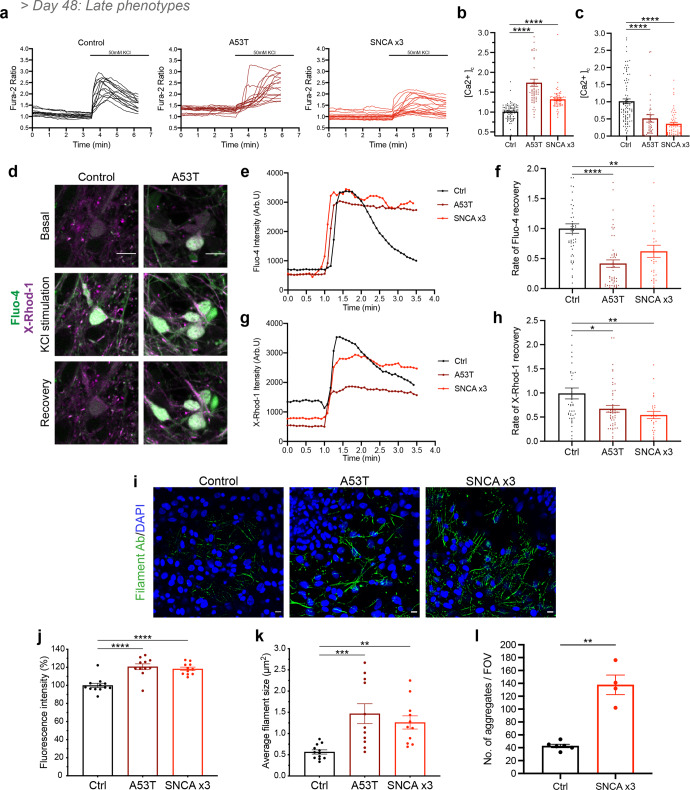
Fig. 5. α-synuclein aggregation and calcium dysregulation persist in older mDA neurons.
a Representative traces showing the Fura-2 ratio in response to 50 mM KCl at day 48 of differentiation in control neurons, A53T neurons, and SNCA x3 neurons. b Quantification of the basal calcium ratio ([Ca2+]c) before KCl stimulation (****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA). c Quantification of the rate of calcium ([Ca2+]c) recovery in response to KCl (****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA). d Representative time series snapshots of >day 48 control and A53T neurons loaded with Fluo-4 (green) and X-Rhod-1 (magenta) (scale bar = 10 μm). e Representative single-cell trace showing delayed recovery of Fluo-4 after KCl stimulation in patient mDA neurons. f Quantification of the normalised rate of recovery of Fluo-4 after stimulation with KCl in >day 48-old neurons (**P = 0.003, ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA). g Representative single-cell trace showing delayed recovery of X-Rhod-1 after KCl stimulation in patient mDA neurons. h Quantification of the normalised rate of recovery of X-Rhod-1 after stimulation with KCl (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, one-way ANOVA). i Representative ICC images showing the expression of aggregated forms of α-synuclein recognised by a conformation-specific antibody, at day 62 of differentiation. Scale bar = 10 μm. j Quantification of the normalised fluorescence intensity of aggregated forms of alpha-synuclein (****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA). k Quantification of the average puncta size of the aggregated alpha-synuclein (**P = 0.0082, ***P = 0.0007, one-way ANOVA). l Quantification showing the number of aggregates per field of view (FOV) from mDA neuronal lysate at day 62 (**P < 0.005, Welch’s t test). All values plotted as ±s.e.m. All N numbers for each experiment can be found in Supplementary Table 5.