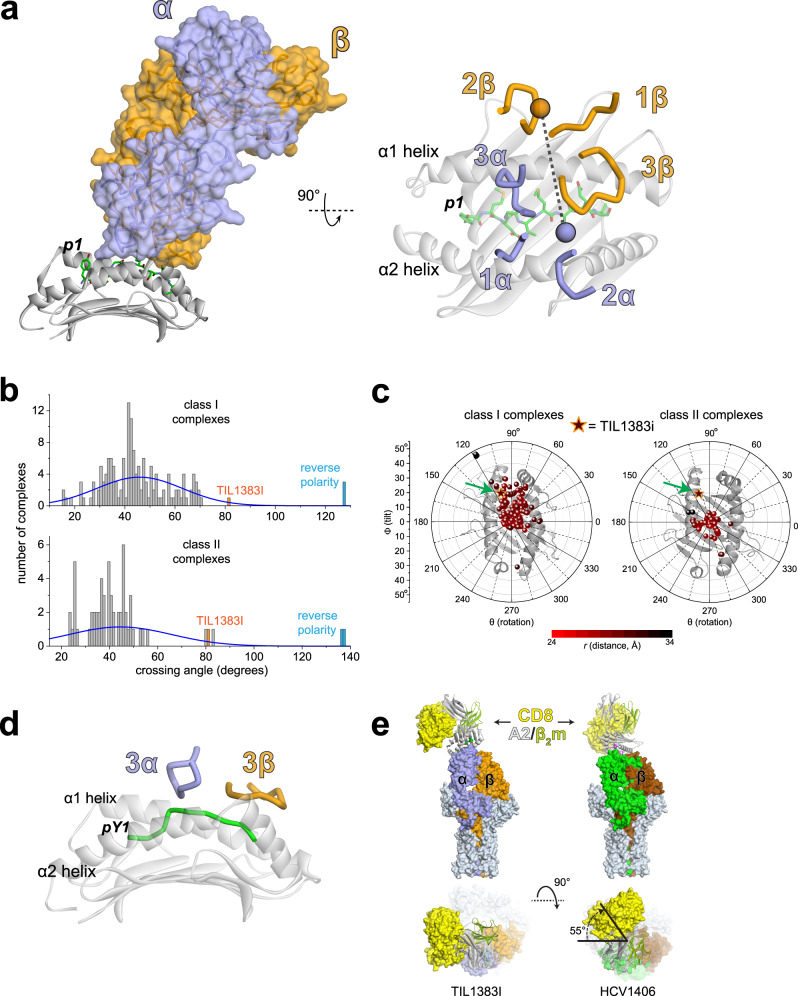
Fig. 2. Structural overview of the TIL1383I-Tyr370D/HLA-A2 complex.
a TIL1383I binds Tyr370D/HLA-A2 counterclockwise compared to traditional TCR-peptide/MHC complexes, placing the germline CDR loops in unusual positions. The left panel shows the overview of the TIL1383I complex. The right panel shows a view of the CDR loops over the peptide/HLA-A2 complex. Circles show the positions of the centers of mass of the TCR variable domains. b Histograms of crossing angles of TCRs bound to class I (top) or class II (bottom) peptide/MHC complexes. The value for TIL1383I, indicated in orange, is more than two standard deviations above the means for both classes. The values at the edges (>120°) are for recently described TCRs that bind with reverse polarity. c Quantitative geometrical analysis indicates that, despite binding atypically, TIL1383I still resembles a class I-restricted TCR in how it accesses the Tyr370D peptide. The position of TIL1383I is indicated by the star, also highlighted by the green arrow. The plots indicate the rotation (θ), tilt (ϕ), and distance (r) of the TCR variable domain COM relative to the MHC peptide-binding groove COM. d The class I-restricted character of TIL1383I revealed in panel c emerges from how the hypervariable CDR3 loops focus on the center and C-terminal bulge of the Tyr370D peptide. e Modeling the structure of the TIL1383I-Tyr370D/HLA-A2 complex and the canonically binding HCV1406-NS3/HLA-A2 complex into the structure of the intact TCR/CD3 complex along with the structure of CD8 bound to HLA-A2 shows an approximate 55° difference in the placement of the CD8 coreceptor relative to the CD3 subunits. Data for panels b and c are provided as a Source Data file.