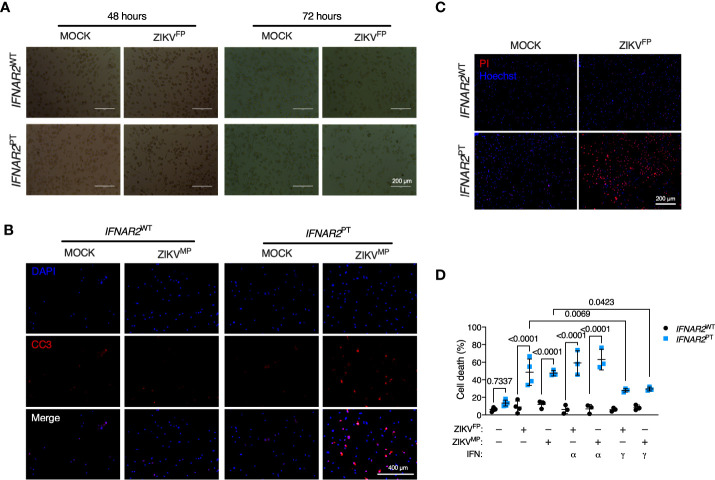
Figure 5.
IFNAR2-deficient iPS-macrophages are vulnerable to ZIKV cytopathic effects. (A) Progressive cytopathicity in IFNAR2 PT (clone 6) but not IFNAR2 WT (WT2) iPS-Mϕ following infection with ZIKVFP MOI = 1.0, showing morphological features of cell shrinkage, membrane blebbing and cell fragmentation. Scale bar, 200 μm. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of cleaved caspase 3 (CC3) at 48 h.p.i. ZIKVMP MOI = 1.0. Representative images of two independent experiments. Scale bar, 400 μm. (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of cell viability showing representative images of cell death at 72 h.p.i. ZIKVFP MOI = 1.0 in IFNAR2 PT (clone 11) but not IFNAR2 WT (WT2) iPS-Mϕ, representative of n = 4 independent experiments. Scale bar, 200 μm. (D) CellProfiler quantification of cell viability assay in IFNAR2 PT (clone 11) and IFNAR2 WT (WT1 and WT2) iPS-Mϕ with or without recombinant IFNα2b or IFNγ (1000 IU/mL) pretreatment. 72 h.p.i. ZIKVFP MOI = 1.0 (n = 4 independent experiments) or ZIKVMP MOI = 1.0 (n = 3 independent experiments). Mean ± SD, ANOVA with Sidak’s test for multiple comparisons.