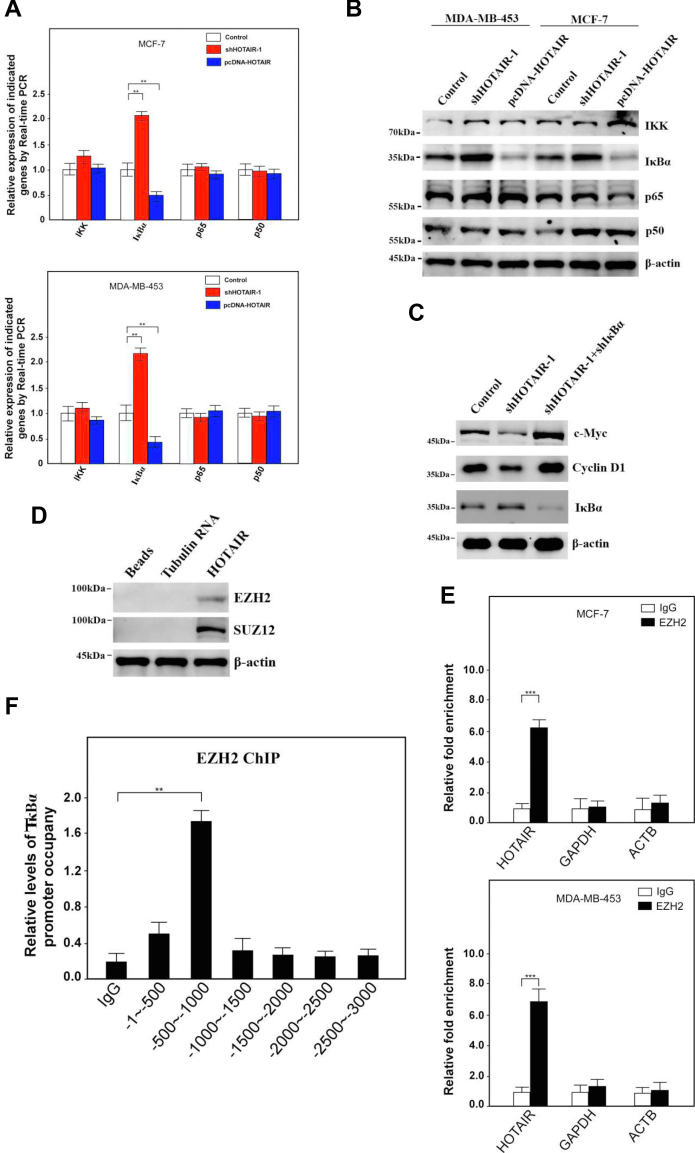
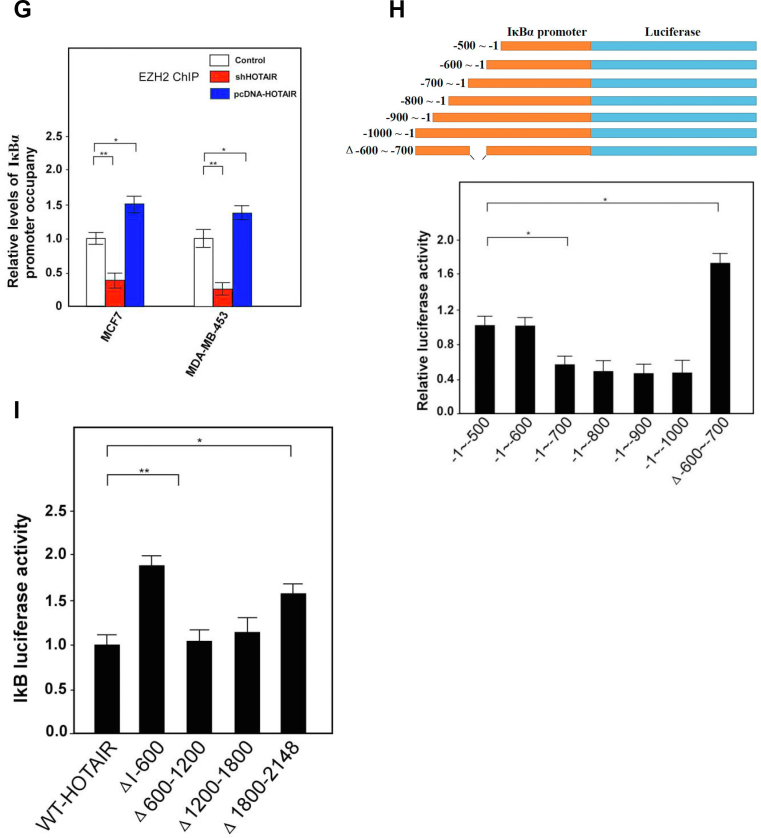
Figure 5.
HOTAIR recruits PRC2 complex onto IκBα promoter to inhibit the gene expression.A, the indicated genes were subjected to the expression analysis by real-time PCR after HOTAIR knockdown or overexpression. Relative gene expression was normalized to endogenous β-actin. Results are shown as means ± SD. B, the indicated genes were subjected to the expression analysis by Western blotting after HOTAIR knockdown or overexpression. β-actin was used as an internal control. C, the indicated genes were subjected to the expression analysis by Western blotting after shHOTAIR transfection alone or along with shIκBα. β-actin was used as an internal control. D, RNA pulldown assay was performed and two core components of the PRC2 were confirmed by immunoblotting. β-actin was used as a loading control. E, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay was performed and the indicated genes were subjected to real-time PCR. F, ChIP-quantitative PCR analysis was performed for the detection of EZH2-binding site in IκBα promoter. Data are shown as means ± SD. G, ChIP-quantitative PCR analysis was performed for the detection of EZH2-binding site in IκBα promoter after HOTAIR knockdown or overexpression. Data are shown as means ± SD. H, different loci of IκBα promoter were constructed into pGL4.18 vector (upper panel) and subjected to luciferase reporter assays (lower panel). Data are shown as means ± SD. I, pGL4.18- IκBα promoter reporter plasmid was transfected into cells with WT HOTAIR or truncated HOTAIR respectively and luciferase activity was measured. EZH2, enhancer of zeste homolog 2; HOTAIR, Hox transcript antisense intergenic RNA; PRC2, polycomb repressive complex 2 (∗ indicates p < 0.05; ∗∗ indicates p < 0.01; ∗∗∗ indicates p < 0.001.).