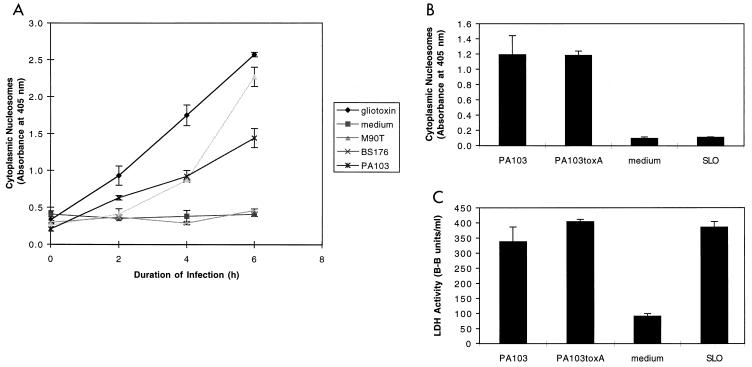
FIG. 2.
Apoptosis of J774A.1 cells infected with PA103. (A) PA103 caused apoptosis of J774A.1 cells in a time-dependent manner as measured by the quantitative assay ELISAPlus. Cells were infected at an MOI of approximately 160. Positive controls included gliotoxin (5 μM) and the virulent S. flexneri strain M90T. Negative controls included medium and the avirulent S. flexneri strain BS176. (B) Apoptosis-inducing capacity of PA103, PA103exsA::Ω, PA103tox::Ω, and SLO, as measured by the quantitative ELISA. Cells were infected for 6 h at an MOI of approximately 160 or exposed to SLO at a concentration of 37.5 μg/ml. (C) Cytotoxicity-inducing capacity of PA103, PA103exsA::Ω, PA103tox::Ω, and SLO, as measured by LDH release assays. Infection conditions were similar to those described in panel B. The ELISA for apoptosis is clearly capable of distinguishing necrotic cell death (SLO) from apoptotic cell death (PA103). Furthermore, exotoxin A does not contribute to PA103-induced apoptosis under the conditions of this assay. Error bars represent standard errors of the means for experiments performed in triplicate.