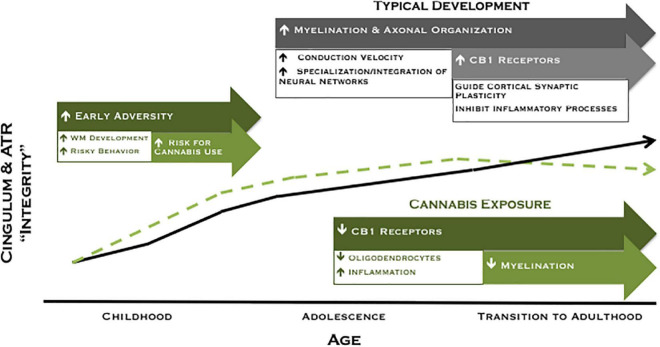
FIGURE 3.
Revised theoretical model of developing ACC connectivity among individuals with and without meaningful cannabis exposure. In typical development (black line), increased myelination, axonal organization, and CB1 receptor expression are postulated to give rise to increased white matter integrity across adolescence and into adulthood. Exposure to adversity early in development may lead to a compensatory acceleration of white matter development, which may increase risky behavior and risk for cannabis use among a subset of individuals (green dashed line). Conversely, cannabis exposure is associated with reduced white matter maturation of the cingulum during the transition to adulthood, an effect that may be mediated by a downregulation of CB1 receptor expression and/or direct effects on oligodendrocyte survival and myelination.