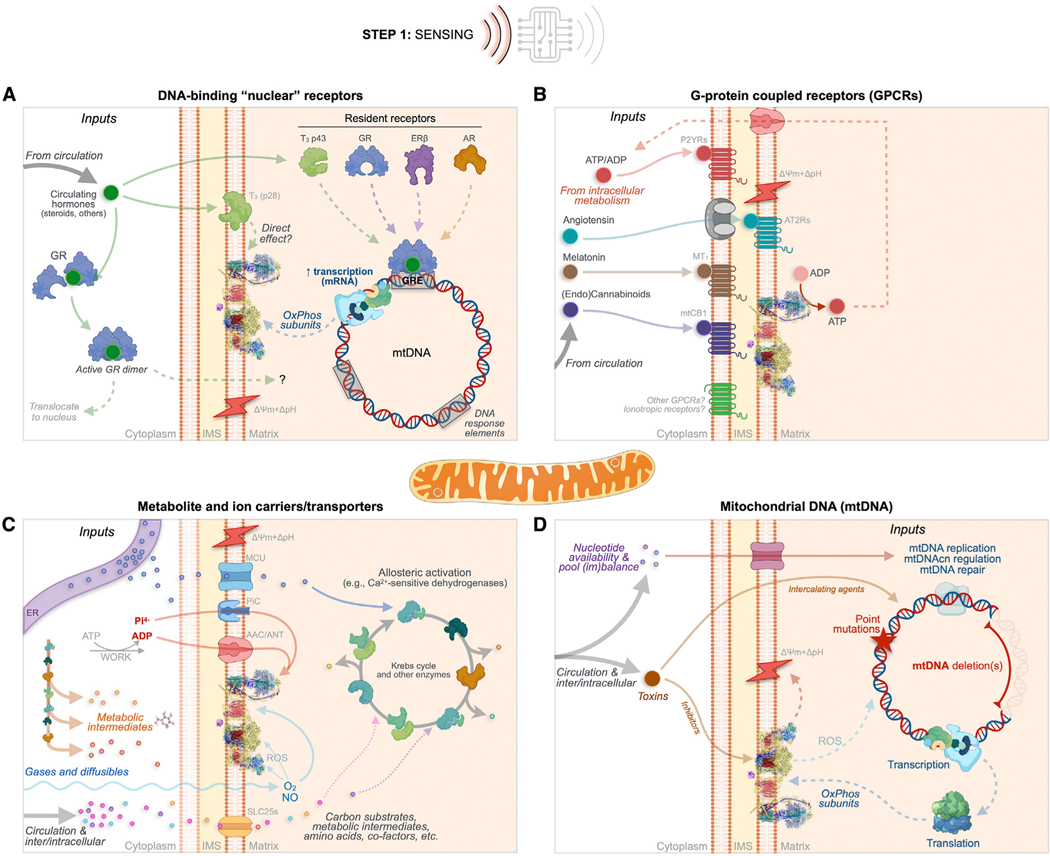
Figure 4. MIPS step 1: Sensing.
As in excitable cells where a broad variety of chemical inputs (e.g., neurotransmitters) converge onto membrane potential variations, extrinsic and intrinsic MIPS inputs trigger molecular changes that converge into morpho-functional mitochondrial states. Mitochondria sense extrinsic and intrinsic information through four main classes of mechanisms.
(A) Canonical DNA-binding “nuclear” receptors for steroid hormones including glucocorticoids (GC), estrogen (ER), and androgen (AR) exist in mitochondria or can translocate upon ligand binding.
(B) G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) embedded within mitochondrial membranes including the angiotensin (AT1R and AT2R), the cannabinoid (mtCB1), melatonin (MT1), and purine (Py2Rs) receptors, and possibly others (e.g., GPR35).
(C) Metabolite and ion carriers/transporters such as the ADP/ATP carrier protein (AAC, also adenine nucleotide translocator [ANT]) and the SLC25 family of transporters. Also shown are some gases and ions that either freely diffuse through the IMM or whose import/export is mediated by other carriers/transporters.
(D) Acquired sequence variation in the mtDNA sequence, including mutations and deletions that cause functional changes within the OxPhos system. The top path shows nucleotide availability/imbalance, and the bottom path shows exogenous toxins that can interfere with electron transport chain function and secondarily cause mtDNA instability.
AAC/ANT, ADP/ATP carrier or adenine nucleotide translocator; AT2Rs, angiotensin receptors; AR, androgen receptor; ERβ, estrogen receptor beta; GR, glucocorticoid receptor; GRE, glucocorticoid response element (used here as an example for other gene regulatory elements); IMS, intermembrane space; MCU, mitochondrial calcium uniporter; mtCB1, mitochondrial cannabinoid receptor; MT1, melatonin 1 receptor; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; NO, nitric oxide; O2, molecular oxygen; OxPhos, oxidative phosphorylation; P2YRs, purine receptors; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SLC25s, solute carriers family 25; T3, triiodothyronine; ΔpH+Δψm, mitochondrial proton motive force.