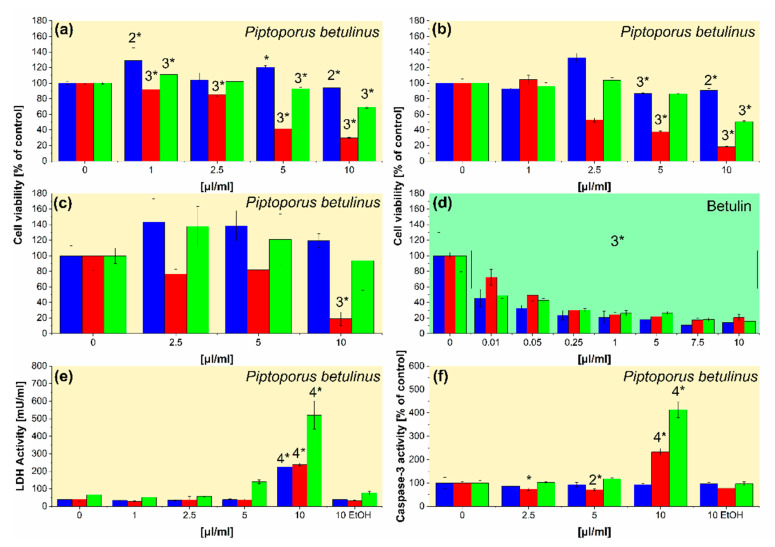
Figure 2.
The effect of Piptoporus betulinus and betulin on Hs27 (blue columns), A375 (red columns), and WM115 (green columns) in terms of (a–d) cell viability, (e) cytotoxicity, and (f) apoptosis. The cells, cultured in 96-well plates, were treated with the ethanolic extracts of Piptoporus betulinus (1, 2.5, 5, and 10 μL mL−1), betulin solution (0.01, 0.05, 0.25, 1, 5, 7.5, and 10 μL mL−1), or the highest concentration (10 μL mL−1) of ethanol (EtOH) for 24 h. Cell viability was evaluated by (a) alamarBlue, (b,d) CellTiter, and (c) ApoTox-Glo assays; cell cytotoxicity was analyzed by (e) LDH test; apoptosis was determined by (f) ApoTox-Glo assay. The results are presented as means ± SD of three repetitions, and asterisked values differ significantly between treated and untreated cells at * p < 0.05, 2* p < 0.01, 3* p < 0.001, and 4* p < 0.0001 as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.