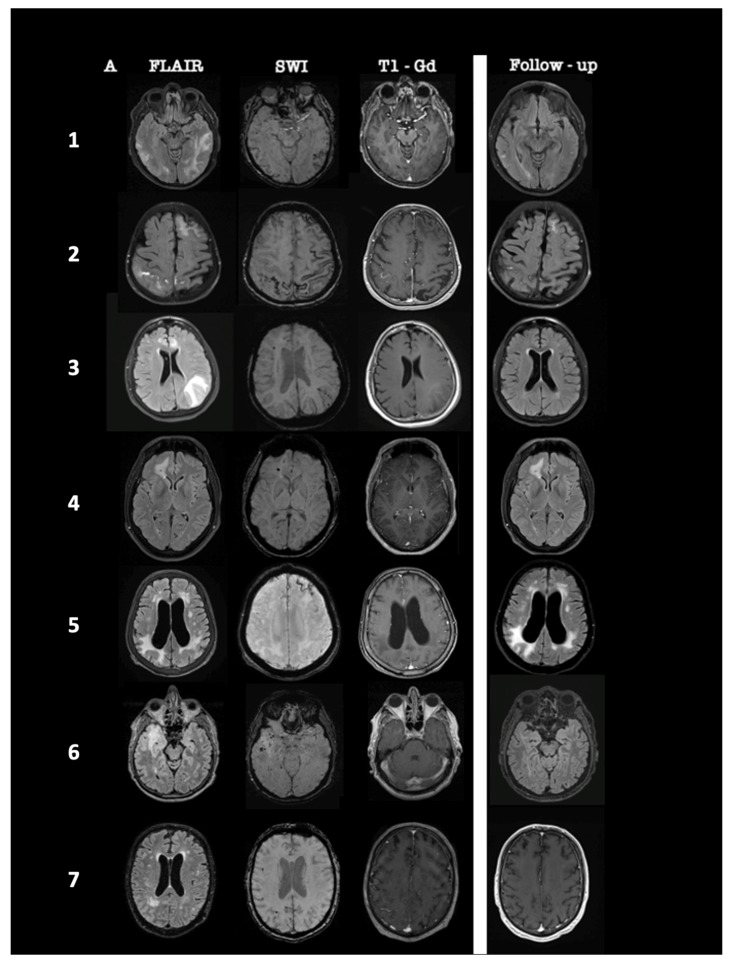
Figure 1.
Summary of brain MRI characteristics of 7 patients at diagnosis and one month after treatment initiation. MRI findings of patients #1 to #7 are ordered from the top to the bottom. At diagnosis, axial fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequences showed supratentorial white matter lesions, multifocal in patients #1, #2, #3, and #5 and unifocal in patients #4, #6, and #7. In patients #1, #3, #4, #6, and #7, these lesions were associated with multiple cortical and subcortical cerebral microbleeds on Susceptibility Weighted Images, whereas patient #2 demonstrated left frontal cortical superficial siderosis (CSS) and subacute cortical subarachnoid hemorrhage (CSAH) on the right parietal lobe, and disseminated CSS was depicted on patient #5. White matter lesions on patients #2, #3, #4, #6, and #7 were associated with parenchymal or leptomeningeal contrast enhancement. In patients #1, #2, #3, #4, #5, and #6, follow-up axial FLAIR sequence one month after corticosteroid initiation showed a marked regression of hyperintense lesions on patients #1, #2, #3, and #6 and a stable size of hyperintense lesions on patients #4 and #5. In patient #7, the follow-up axial post-gadolinium T1 sequence revealed a complete resolution of gadolinium enhancement.