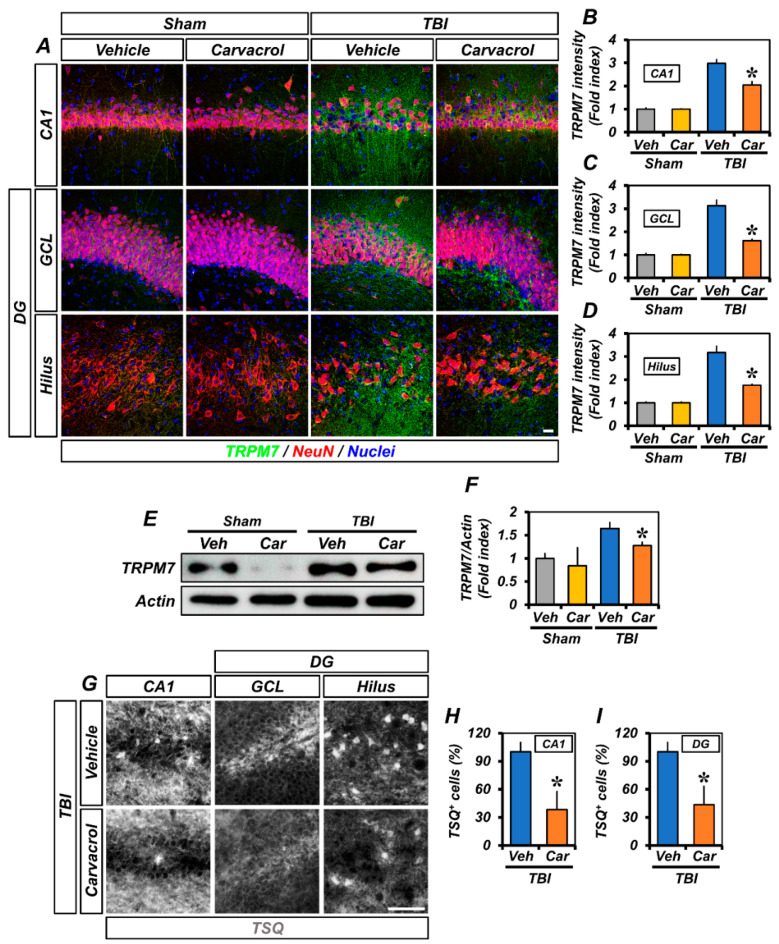
Figure 1.
Carvacrol reduced TRPM7 over-expression and intracellular free zinc accumulation after TBI: (A) Double-label confocal micrographs representing neuronal marker NeuN+ neuronal nuclei (red) co-labeled with the TRPM7 (green) in the CA1, GCL, and hilus of ipsilateral hippocampus from vehicle- and carvacrol-treated groups 12 h after sham surgery or TBI. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 µm; (B–D) quantification of the immunofluorescence intensity of TRPM7 (green), as determined in the same CA1 (B), GCL (C), and hilus (D) regions of the ipsilateral hippocampus (mean ± SEM; n = 3–6 per group). * p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated TBI group (Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Bonferroni posthoc test: CA1: Chi square = 14.294, df = 3, p = 0.003; GCL: Chi square = 14.294, df = 3, p = 0.003; hilus: Chi square = 14.399, df = 3, p = 0.002); (E) Western blot of TRPM7 in the ipsilateral hippocampus; (F) bar graphs showing the quantification of TRPM7 protein amounts from the ipsilateral hippocampus (mean ± SEM; n = 3–4 per group). * p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated TBI group (Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test: CA1: Chi square = 8.71, df = 3, p = 0.0334); (G) representative images showing sections of the ipsilateral hippocampus stained with TSQ for the detection of the accumulation of intracellular free zinc. Scale bar, 25 µm; and (H,I) bar graphs showing the number of TSQ+ neurons in the CA1 (H) and DG (I) of the ipsilateral hippocampus (mean ± SEM; n = 3 per group). * p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated TBI group (unpaired Student’s t-test).