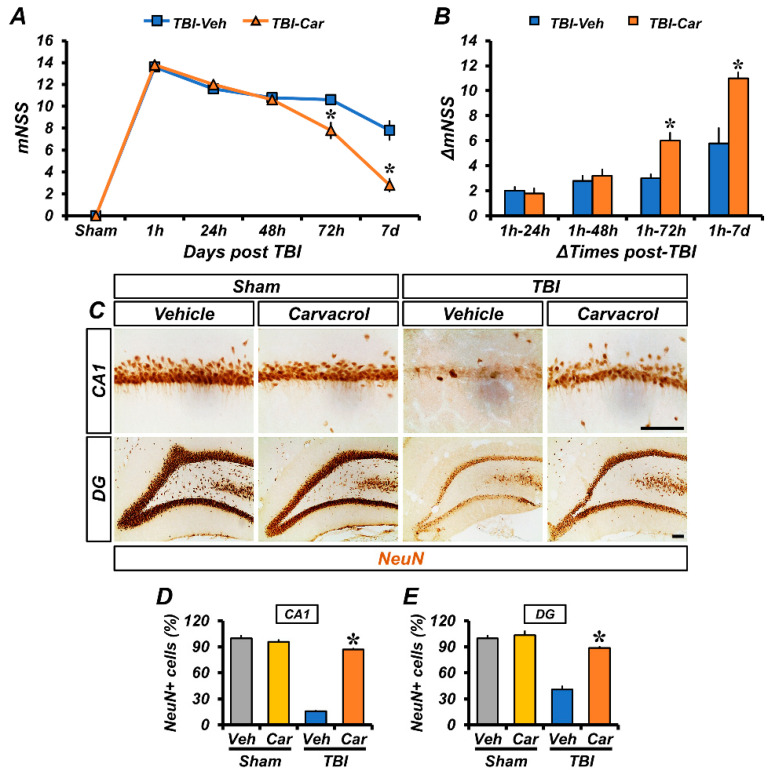
Figure 6.
Carvacrol not only improved neurological function but also reduced neuronal death after TBI: (A) The mNSS was determined in rats at 1, 24, 48, 72 h, and 7 days after TBI. A score of 18 means that all tasks were failed; a score of 0 means that all tasks were successfully completed (mean ± SEM; n = 5 per group). * p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated TBI group (repeated measures ANOVA; Time: F = 583.733, p < 0.001; Group: F = 2.4, p = 0.016; Time × Group interaction: F = 8.882, p < 0.001); (B) changes in mNSS (ΔmNSS) were assessed at various time intervals between the 1 h and multiple pre-determined time points thereafter (mean ± SEM; n = 5 per group). * p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated TBI group (repeated measures ANOVA; Time: F = 74.780, p < 0.001; Group: F = 12.041, p = 0.008; Time × Group interaction: F = 14.363, p < 0.001); (C) photomicrographs showing sections of the hippocampal CA1 and DG stained for the neuronal marker NeuN, scale bar, 100 μm; (D,E) bar graphs showing the number of NeuN+ neurons in the hippocampal CA1 (D) and DG (E) areas (mean ± SEM; n = 3–6 per group). * p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated TBI group (Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test: CA1: Chi square = 13.459, df = 3, p = 0.004; DG: Chi square = 13.243, df = 3, p = 0.004).