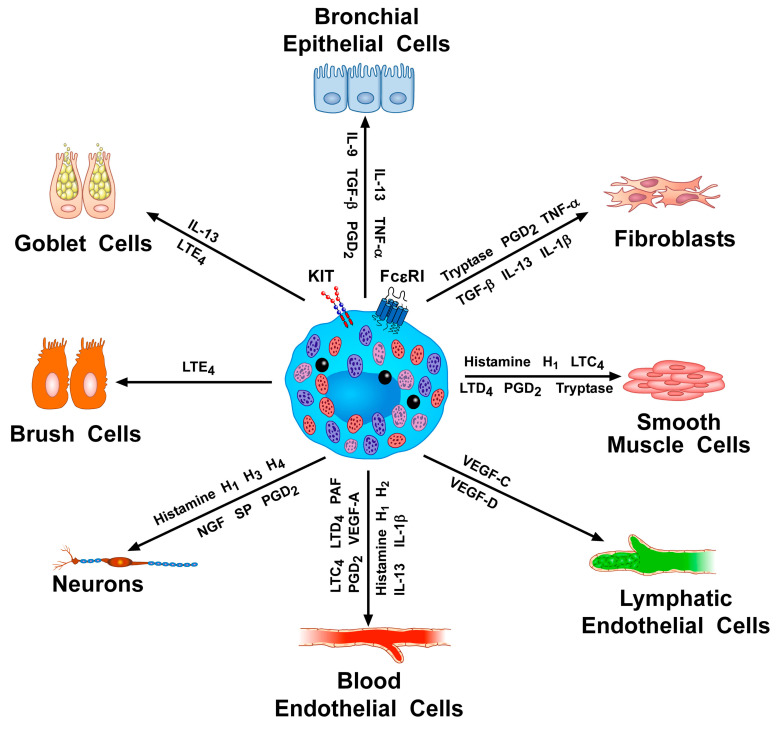
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the multiple interactions between human lung mast cells and various non-immune cells through the release of mediators. Mast cells can interact with bronchial epithelial cells (IL-13, TNF-α, IL-9, TGF-β, and PGD2), brush cells (LTE4), fibroblasts (tryptase, PGD2, TNF-α, TGF-β, IL-13, and IL-1β), smooth-muscle cells (histamine, LTC4, LTD4, PGD2, and tryptase), goblet cells (IL-13 and LTE4), blood endothelial cells (histamine, LTC4, LTD4, PGD2, PAF, VEGF-A, IL-13, and IL-1β), lymphatic endothelial cells (VEGF-C and VEGF-D), and neurons (histamine, NGF, SP, and PGD2). Modified with permission from Varricchi 2019 [151].