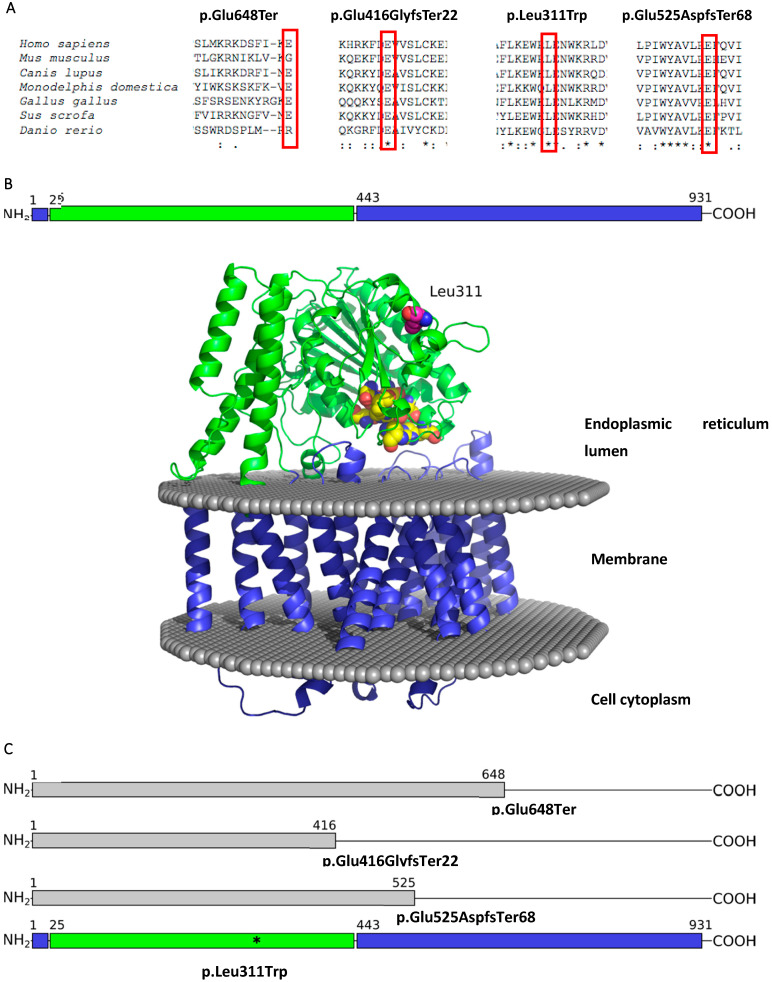
Figure 2.
(A) Multiple sequence alignment produced by ClustalO of the PIGN protein across seven evolutionarily distant species. Below the amino acid sequences is a key denoting conserved sequence (*), conservative variants (:), semi-conservative variants (.), and non-conservative variants (); (B) The domain organization and structure model of human PIGN protein. The membrane region is coloured in blue, the lumenal domain is green, mutated residue Leu311 is shown in magenta coloured spheres, conserved residues that are likely to belong to enzyme active site are shown in yellow spheres; (C) Pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants visualized on the protein sequence.